Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Two particles A and B, each with a charge Q, are placed a distance d apart. Where should a particle of charge q be placed on the perpendicular bisector of AB, so that it experiences maximum force? What is the magnitude of this maximum force?
उत्तर
Let the charge q be placed at a distance x on the perpendicular bisector of AB.
As shown in the figure, the horizontal component of force is balanced.
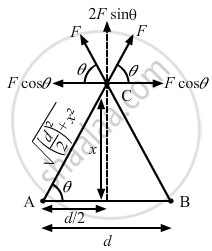
\[\sin\theta = \frac{x}{\sqrt{\left( \frac{d}{2} \right)^2 + x^2}}\]
Total vertical component of force,
\[F' = 2F\sin\theta\]
\[F' = 2 \times \frac{1}{4\pi \epsilon_0} \times \frac{qQ}{\left( \frac{d}{2} \right)^2 + x^2} \times \frac{x}{\sqrt{\left( \frac{d}{2} \right)^2 + x^2}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow F' = \frac{1}{2\pi \epsilon_0} \times \frac{qQx}{\left[ \left( \frac{d}{2} \right)^2 + x^2 \right]^{3/2}}\]
For maximum force, \[\frac{dF'}{dx} = 0\]
\[\frac{qQ}{2\pi \epsilon_0} \times \left[ \left[ \left( \frac{d}{2} \right)^2 + x^2 \right]^{- 3/2} - x\frac{3}{2} \left[ \left( \frac{d}{2} \right)^2 + x^2 \right]^{- 5/2} 2x \right] = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow \left( \frac{d}{2} \right)^2 + x^2 - 3 x^2 = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2 x^2 = \left( \frac{d}{2} \right)^2 \]
\[ \Rightarrow x = \frac{d}{2\sqrt{2}}\]
\[ \therefore F '_\max = \frac{1}{2\pi \epsilon_0}\frac{qQ\frac{d}{2\sqrt{2}}}{\left[ \left( \frac{d}{2} \right)^2 + \left( \frac{d}{2\sqrt{2}} \right)^2 \right]^{3/2}}\]
\[ = 3 . 08\frac{Qq}{4\pi \epsilon_0 d^2}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
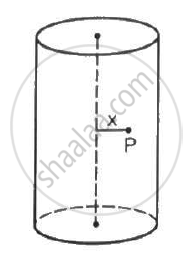
A long cylindrical volume contains a uniformly distributed charge of density ρ. Find the electric field at a point P inside the cylindrical volume at a distance x from its axis (see the figure).
Two large conducting plates are placed parallel to each other with a separation of 2⋅00 cm between them. An electron starting from rest near one of the plates reaches the other plate in 2⋅00 microseconds. Find the surface charge density on the inner surfaces.
Two particles A and B with charges q and 2q, respectively, are placed on a smooth table with a separation d. A third particle C is to be clamped on the table in such a way that the particles A and B remain at rest on the table under electrical forces. What should be the charge on C and where should it be clamped?
A positive charge Q is distributed uniformly over a circular ring of radius R. A particle of mass m, and a negative charge q, is placed on its axis at a distance x from the centre. Find the force on the particle. Assuming x << R, find the time period of oscillation of the particle if it is released from there .
A positively charged glass rod is brought close to a metallic rod isolated from ground. The charge on the side of the metallic rod away from the glass rod will be ______.
Two small spheres 18 cm apart have equal negative charges and repel each other with the force of 6 × 10-3 N. Find the total charge on both spheres.
One metallic sphere A is given a positive charge whereas another identical metallic sphere B of exactly the same mass as A is given an equal amount of negative charge. Then
When 1019 electrons are removed from a neutral metal plate through some process, the electric charge on it is ______
A conducting sphere of radius 0.104 m has an unknown charge. If the electric field at 0.20 m from the centre of the sphere is 1.5 x 103 NC-1 and points radially inward, what is the electric flux?
Electric charge is a property of ______.
Conductors are materials that allow ______.
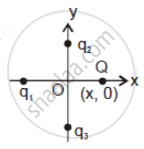
In figure two positive charges q2 and q3 fixed along the y-axis, exert a net electric force in the + x-direction on a charge q1 fixed along the x-axis. If a positive charge Q is added at (x, 0), the force on q1 ______.
(1) |
(2) |
A solid sphere of radius R1 and volume charge density `rho = rho_0/"r"` is enclosed by a hollow sphere of radius R2 with negative surface charge density σ, such that the total charge in the system is zero. `rho_0` is a positive constant and r is the distance from the center of the sphere. The ratio R2/R1 is ______.
Which of the following graphs shows the variation of electric field E due to a hollow spherical conductor of radius R as a function of distance from the centre of the sphere?
Which one of the following is the unit of electric charge?
Two identical metallic spheres A and B when placed at certain distance in air repel each other with a force of F. Another identical uncharged sphere C is first placed in contact with A and then in contact with B and finally placed at midpoint between spheres A and B. The force experienced by sphere C will be:
A straight infinitely long cylinder of radius R0 = 10 cm is uniformly charged with a surface charge density σ = + 10-12 C/m2. The cylinder serves as a source of electrons, with the velocity of the emitted electrons perpendicular to its surface. Electron velocity must be ______ × 105 m/s to ensure that electrons can move away, from the axis of the cylinder to a distance greater than r = 103 m.
