Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A ray of light is incident on a plane mirror making an angle of 90° with the mirror surface. The angle of reflection for this ray of light will be:
(a) 45°
(b) 90°
(c) 0°
(d) 60°
उत्तर
(c) 0o, since angle of incidence = 0o .
According to the first law of reflection, the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
It is desired to obtain an erect image of an object, using concave mirror of focal length of 12 cm.
Where will the image of this object be, if it is placed 24 cm in front of the mirror? Draw ray diagram for this situation also justify your answer. Show the positions of pole, principal focus and the centre of curvature in the above ray diagrams
A student has obtained the image of a distant object with a concave mirror to determine its focal length. If he has selected a well-illuminated red building as object, which of the following correctly describes the features of the image formed?
(A) Virtual, inverted and diminished image in red shade
(B) Real, erect and diminished image in pink shade
(C) Real, inverted and diminished image in red shade
(D) Virtual, erect and enlarged image in red shade
A spherical mirror produces an image of magnification −1 on a screen placed at a distance of 40 cm from the mirror:
(i) Write the type of mirror.
(ii) What is the nature of the image formed?
(iii) How far is the object located from the mirror?
(iv) Draw the ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
At what distance from a concave mirror focal length 10 cm should an object 2 cm long be placed in order to get an erect image 6 cm tall?
A converging mirror forms a real image of height 4 cm of an object of height 1 cm placed 20 cm away from the mirror:
- Calculate the image distance.
- What is the focal length of the mirror?
A concave mirror produces three times enlarged virtual image of an object placed at 10 cm in front of it. Calculate the radius of curvature of the mirror.
If the image formed is always virtual, the mirror can be:
(a) concave or convex
(b) concave or plane
(c) convex or plane
(d) only convex
An object is placed 15 cm from (a) a converging mirror, and (b) a diverging mirror, of radius of curvature 20 cm. Calculate the image position and magnification in each case.
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object placed on the principal axis of a convex mirror. State the position, size and nature of the image. What happens to the image as the object is moved away from the mirror?
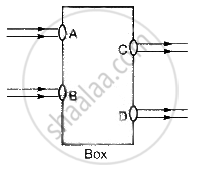
Beams of light are incident through the holes A and B and emerge out of box through the holes C and D respectively as shown in the figure. Which of the following could be inside the box?