Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A ray PQ incident normally on the refracting face BA is refracted in the prism BAC made of material of refractive index 1.5. Complete the path of ray through the prism. From which face will the ray emerge? Justify your answer.
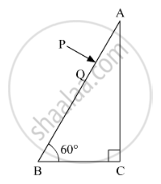
उत्तर
Here,
`sin i_c=2/3=0.66`
`=>sin 30^0=0.5`
ic > 300
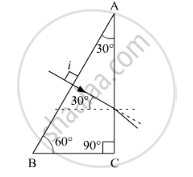
Thus, here light will emerge out from face AC.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
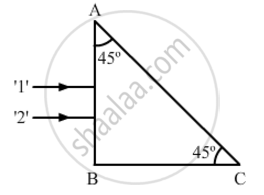
Two monochromatic rays of light are incident normally on the face AB of an isosceles right-angled prism ABC. The refractive indices of the glass prism for the two rays '1' and '2' are respectively 1.38 and 1.52. Trace the path of these rays after entering through the prism.
What is a dispersion of light
Describe an activity to show that the colours of white light splitted by a glass prism can be recombined to get white light by another identical glass prism. Also, draw a ray diagram to show the recombination of the spectrum of white light.
Give the formula that can be used to determine refractive index of materials of a prism in minimum deviation condition ?
If three identical prisms are combined, is it possible to pass a beam that emerges undeviated? Undispersed?
If a glass prism is dipped in water, its dispersive power ___________ .
A thin prism of angle 6.0°, ω = 0.07 and μy = 1.50 is combined with another thin prism having ω = 0.08 and μy = 1.60. The combination produces no deviation in the mean ray. (a) Find the angle of the second prism. (b) Find the net angular dispersion produced by the combination when a beam of white light passes through it. (c) If the prisms are similarly directed, what will be the deviation in the mean ray? (d) Find the angular dispersion in the situation described in (c).
In a regular prism, what is the relation between angle of incidence and angle of emergence when it is in the minimum deviation position?
An equilateral glass prism has a refractive index 1.6 in the air. Calculate the angle of minimum deviation of the prism, when kept in a medium of refractive index `4sqrt(2)"/"5.`
Prove that in case of a prism, i + e = A + δ, where the symbols have their usual meanings.
