Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A small hole of changing diameter at the centre of Iris is called _______.
विकल्प
optic nerves
cornea
optic disc
pupil
उत्तर
A small hole of changing diameter at the centre of Iris is called pupil.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The human eye can focus objects at different distances by adjusting the focal length of the eye lens. This is due to ______.
Compare the following: Choroid and retina
Explain the following:
Mechanism of generation of light-induced impulse in the retina.
Distinguish between: aqueous humor and vitreous humor
Explain, why a normal eye is not able to see distinctly the objects placed closer than 25 cm, without putting any strain on the eye.
What is the function of the lens in the human eye?
What is the:
far point of a normal human eye?
What changes take place in the shape of eye-lens:
when the eye is focused on a distant object?
The eyes of a person are focused (i) on a nearby object, and (ii) on a distant object, turn by turn. In which case:
the focal length of eye-lens will be the maximum?
A person walking in a dark corridor enters into a brightly lit room:
State the effect on the pupil of the eye.
There are two types of light-sensitive cells in the human eye:
Where are they found?
There are two types of light-sensitive cells in the human eye:
What is each type called?
There are two types of light-sensitive cells in the human eye:
To what is each type of cell sensitive?
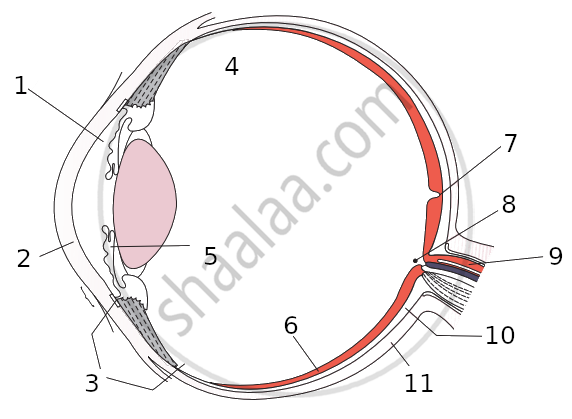
Draw a simple diagram of the human eye and label clearly the cornea, iris, pupil, ciliary muscles, eye-lens, retina, optic nerve and blind spot.
The size of the pupil of the eye is adjusted by:
(a) cornea
(b) ciliary muscles
(c) optic nerve
(d) iris
Which part brings the image into sharp focus on the retina? How does it do this?
An object is moved closer to an eye. What changes must take place in the eye in order to keep the image in sharp focus?
With both eyes open, a person's field of view is about:
(a) 90°
(b) 150°
(c) 180°
(d) 360°
The animals of prey have:
(a) two eyes at the front
(b) two eyes at the back
(c) two eyes on the sides
(d) one eye at the front and one on the side
Define the following:
Power of accommodation
Name the following:
The pigmented circular area seen in the eye.
Give Technical Term:
The cells of the retina that are sensitive to colour.
State the Function:
Cornea
The image of an object at an infinite distance is obtained in a real and erect form through a convex magnifying glass.
Write scientific reason.
The movie cannot be enjoyed if seat of a viewer is too close to the screen in the cinema.
Write the function of the human eye and label parts of the figure given below.

Complete the paragraph by choosing the right options given below.
(minimum, near point, 25 cm, farthest, farthest distance, far point)
The _______ distance of an object from a normal eye, at which it is clearly visible without stress on the eye, is called the minimum distance of distinct vision. The position of the object at this distance is called the _______ of the eye, for a normal human eye, the near point is at _______. The _______ distance of an object from a human eye, at which it is clearly visible without stress on the eye is called _______ of distinct vision. The position of the object at this distance is called the _______ of the eye.
______ is tough and thick white sheath that protects the inner parts of the eye.
Why the human eye is compared with camera?
Write down the names of parts of the eye in the blank spaces shown in the figure.

The coloured portion of the eye is the ______.
Select the option with incorrect identification:
In human eye the part which allows light to enter into the eye is ______.
Match the following:
| Column - I | Column - II |
| 1. Retina | a. Path way of light |
| 2. Pupil | b. Far point comes closer |
| 3. Ciliary muscles | c. near point moves away |
| 4. Myopia | d. Screen of the eye |
| 5. Hypermetropia | e. Power of accommodation |
With reference to human eye, answer the following question.
What is aqueous humor?
Arrange and rewrite the term in group in correct order to be in a logical sequence, beginning with the term that is underlined:
Pupil, Aqueous humour, Retina, Vitreous humour.
Match the following:
| Column - I | Column - II | ||
| 1 | Retina | a | Path way of light |
| 2 | Pupil | b | Far point comes closer |
| 3 | Ciliary muscles | c | near point moves away |
| 4 | Myopia | d | Screen of the eye |
| 5 | Hypermetropoia | e | Power of accomodation |
Match the following.
| Column - I | Column - II | ||
| 1 | Retina | a | Path way of light |
| 2 | Pupil | b | Far point comes closer |
| 3 | Ciliary muscles | c | near point moves away |
| 4 | Myopia | d | screen of the eye |
| 5 | Hypermetropia | e | Power of accomadation |
The layer in the eye where sensory cells (rods and cones) are located ______.
Match the following:
| Column - I | Column - II |
| 1. Retina | a. Path way of light |
| 2. Pupil | b. Far point comes closer |
| 3. Ciliary muscles | c. near point moves away |
| 4. Myopia | d. Screen of the eye |
| 5. Hypermetropia | e. Power of accommodation |
