Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
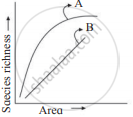
A species-area curve is drawn by plotting the number of species against the area. How is it that when a very large area is considered the slope is steeper than that for smaller areas?
उत्तर
Ecologists have discovered that the value of Z (slope of the line) lies in the range of 0.1 to 0.2, regardless of the taxonomic group or the region (whether it is the plants in Britain, birds in California or molluscs in New York state, the slopes of the regression line are amazingly similar). But, if you analyse the species-area relationships among very large areas like the entire continents, you will find that the slope of the line is much steeper (Z values in the range of 0.6 to 1.2). For example, for frugivorous (fruit-eating) birds and mammals in the tropical forests of different continents, the slope is found to be 1.15.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain, giving three reasons, why tropics show greatest levels of species diversity.
Give three hypotheses for explaining why tropics show greatest levels of species richness.
Observe the graph and select the correct option:
The 'rivet' in the rivet popper hypothesis is considered to represent the ______.
Latitudinal and altitudinal gradient is shown by which of the following habitat(s)?
With reference to graph select the correct alternative
Which of the following is an observation of Alexander von Humboldt's documented pattern in ecology?
Select the correct alternative for x and y.
Amongst the animal group given below, which one has the highest percentage of endangered species?
For frugivorous (fruit-eating) birds and mammals in the tropical forests of different continents, the slope of the species-area relationship is found to be approximately ______.
