Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A stone is tied to one end of a string. Holding the other end, the string is whirled in a horizontal plane with progressively increasing speed. It breaks at some speed because ______
विकल्प
The gravitational forces of the earth are greater than the tension in the string
The required centripetal force is greater than the tension sustained by the string
The required centripetal force is lesser than the tension in the string
The centripetal force is greater than the weight of the stone
उत्तर
A stone is tied to one end of a string. Holding the other end, the string is whirled in a horizontal plane with progressively increasing speed. It breaks at some speed because The required centripetal force is greater than the tension sustained by the string.
संबंधित प्रश्न
State the law of conservation of angular momentum and explain with a suitable example.
Define moment of inertia. State its SI unit and dimensions.
A flywheel of mass 8 kg and radius 10 cm rotating with a uniform angular speed of 5 rad/sec about its axis of rotation, is subjected to an accelerating torque of 0.01 Nm for 10 seconds. Calculate the change in its angular momentum and change in its kinetic energy.
An electron(e) is revolving in a circular orbit of radius r in the hydrogen atom. The angular momentum of the electron is (M = magnetic dipole moment associated with it and m = mass of electron)
A stone of mass 1 kg is rotated in a horizontal circle of radius 0.5 m. If it makes `100/pi` rps, then its angular momentum is ______
A charged particle (charge = q: mass = m) is rotating in a circle of radius 'R' with uniform speed 'v'. The ratio of its magnetic moment (M) to the angular momentum (L) is ______
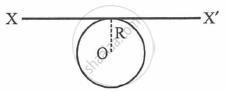
A thin metal wire of length 'L' and uniform linear mass density 'ρ' is bent into a circular coil with 'O' as centre. The moment of inertia of a coil about the axis XX' is ______.
The angular momentum of electron in hydrogen atom is proportional to ____________.
The ratio of the dimensions of Planck's constant to that of moment of inertia is the dimensions of ______.
A particle of mass m is rotating in a plane in a circular path of radius r. Its angular momentum is L. The centripetal force acting on the particle is ______.
Let I1 and I2 be the moments of inertia of two bodies of identical geometrical shape. If the first body is made of aluminium and the second of iron, then ____________.
mass is whirled in a circular path with constant angular velocity and its linear velocity is v. If the string is now halved keeping the angular momentum same, the linear velocity is ______.
An electron has a mass of 9.1 x 10-31 kg. It revolves round the nucleus in a circular orbit of radius 0.529 x 10-10 metre at a speed of 2.2 x 106 m/s. The magnitude of its linear momentum in this motion is ____________.
The direction of angular momentum of particle is ____________.
An electron of mass 'm' revolving around the nucleus in a circular orbit of radius 'r' has angular momentum 'L'. The magnetic field produced by the electron at the centre of the orbit is e = electric charge, µ0 = permeability of free space ____________.
A particle is revolving in anticlockwise sense along the circumference of a circle of radius 'r' with linear velocity 'v', then the angle between 'v' and angular velocity 'ω' will be ______.
If E, M and P are the kinetic energy, mass and linear momentum of a particle respectively, which of the following relations represents the angular momentum L of the particle when the particle rotates in a circle of radius R?
lf 'I' is the moment of inertia and 'L' is angular momentum of a rotating body, then `L^2/(2I)` is its ______.
A body is rotating about its own axis. Its rotational kinetic energy is x and its angular momentum is y, hence its moment of inertia about the axis is ______.
A particle of mass m = 5 unit is moving with a uniform speed v = 3`sqrt2` unit in the XY-plane along the line y = x + 4. The magnitude of the angular momentum about origin is ______.
The difference in the angular momentum of an electron in two successive orbits of a hydrogen atom is ______.
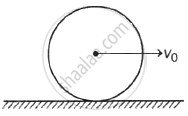
A sphere rolls without slipping on a rough horizontal surface with centre of mass speed v0. If mass of the sphere is M and its radius is R, then what is the angular momentum of the sphere about the point of contact?
The angular momentum of the electron in the second orbit of hydrogen atom is L. The angular momentum in the third orbit is ______.
Define angular momentum.
