Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
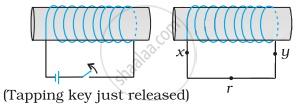
A wire in the form of a tightly wound solenoid is connected to a DC source, and carries a current. If the coil is stretched so that there are gaps between successive elements of the spiral coil, will the current increase or decrease? Explain.
उत्तर
This law gives the direction of induced emf/induced current. According to this law, the direction of induced emf or current in a circuit is such as to oppose the cause that produces it. This law is based upon the law of conservation of energy.
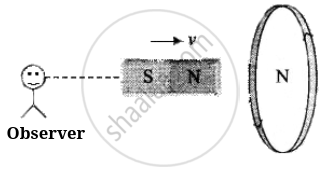
- When AT-pole of a bar magnet moves towards the coil, the flux associated with the loop increases and an emf is induced in it. Since the circuit of loop is closed, induced current also flows in it.
- Cause of this induced current is approach of north pole and therefore to oppose the cause, i.e., to repel the approaching north pole, the induced current in loop is in such a direction so that the front face of loop behaves as north pole. Therefore induced current as seen by observer O is in anticlockwise direction (figure).
According to the given situation as the coil is stretched so that there are gaps between successive elements of the spiral coil, i.e., the wires are pulled apart which leads to the flux leak through the gaps.
According to Lenz’s law, the emf induced in these spirals must oppose this decrease in magnetic flux, which can be done by an increase in current. So, the current will increase.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State Lenz's law. Illustrate, by giving an example, how this law helps in predicting the direction of the current in a loop in the presence of a changing magnetic flux.
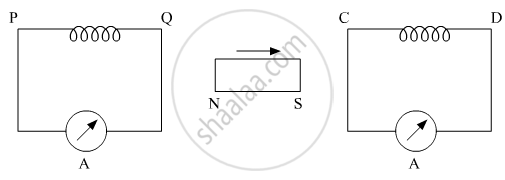
A bar magnet is moved in the direction indicated by the arrow between two coils PQ and CD. Predict the directions of induced current in each coil.
A short magnet is moved along the axis of a conducting loop. Show that the loop repels the magnet if the magnet is approaching the loop and attracts the magnet if it is going away from the loop.
The battery discussed in the previous question is suddenly disconnected. Is a current induced in the other loop? If yes, when does it start and when does it end? Do the loops attract each other or repel?
A bar magnet is moved along the axis of a copper ring placed far away from the magnet. Looking from the side of the magnet, an anticlockwise current is found to be induced in the ring. Which of the following may be true?
(a) The south pole faces the ring and the magnet moves towards it.
(b) The north pole faces the ring and the magnet moves towards it.
(c) The south pole faces the ring and the magnet moves away from it.
(d) The north pole faces the ring and the magnet moves away from it.
2 A 40 kg boy whose legs are 4 cm in area and 50 cm long falls through a height of 2 m without breaking his leg bones. If the bones can withstand stress of 0.9 x 108 N/m2. The Young's modulus for the material of the bone is ______.
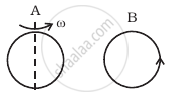
There are two coils A and B as shown in figure. A current starts flowing in B as shown, when A is moved towards B and stops when A stops moving. The current in A is counterclockwise. B is kept stationary when A moves. We can infer that ______.

Same as problem 4 except the coil A is made to rotate about a vertical axis (figure). No current flows in B if A is at rest. The current in coil A, when the current in B (at t = 0) is counterclockwise and the coil A is as shown at this instant, t = 0, is ______.
Predict the direction of induced current in the situation described by the following figure.
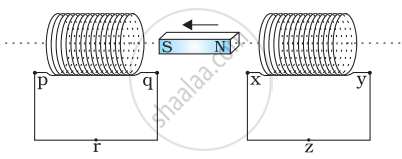
Predict the direction of induced current in the situation described by the following figure.