Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
ABCD is quadrilateral.
Is AB + BC + CD + DA < 2 (AC + BD)?
उत्तर
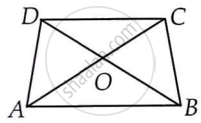
In a triangle, the sum of the lengths of either two sides is always greater than the third side.
Considering ΔOAB,
OA + OB > AB ...(i)
In ΔOBC,
OB + OC > BC ...(ii)
In ΔOCD,
OC + OD > CD ...(iii)
In ΔODA,
OD + OA > DA ...(iv)
Adding equations (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv), we obtain
OA + OB + OB + OC + OC + OD + OD + OA > AB + BC + CD + DA
2OA + 2OB + 2OC + 2OD > AB + BC + CD + DA
2OA + 2OC + 2OB + 2OD > AB + BC + CD + DA
2(OA + OC) + 2(OB + OD) > AB + BC + CD + DA
2(AC) + 2(BD) > AB + BC + CD + DA
2(AC + BD) > AB + BC + CD + DA
Yes, the given expression is true.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Is it possible to have a triangle with the following sides?
3 cm, 6 cm, 7 cm
Is it possible to have a triangle with the following sides?
6 cm, 3 cm, 2 cm
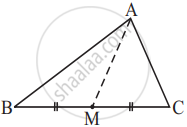
AM is a median of a triangle ABC.
Is AB + BC + CA > 2 AM?
(Consider the sides of triangles ΔABM and ΔAMC.)
ABCD is quadrilateral.
Is AB + BC + CD + DA > AC + BD?

The lengths of two sides of a triangle are 12 cm and 15 cm. Between what two measures should the length of the third side fall?
Is there a triangle whose sides have lengths 10.2 cm, 5.8 cm, and 4.5 cm?
In ∆PQR ______.
The length of two sides of a triangle are 7 cm and 9 cm. The length of the third side may lie between ______.
Sum of two sides of a triangle is greater than or equal to the third side.
Sum of any two angles of a triangle is always greater than the third angle.
