Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
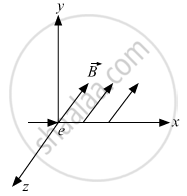
An electron moves along +x direction. It enters into a region of uniform magnetic field. `vecB` directed along –z direction as shown in fig. Draw the shape of the trajectory followed by the electron after entering the field.
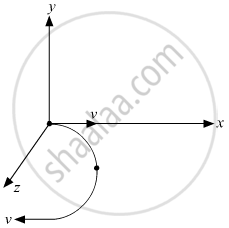
उत्तर
Force on the electron is given by
`vec"F" = -"q"(vec"v" xx vec"B")`
So, the electron will follow a semi-circular path in the magnetic field.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Solve the following problem.
Two small and similar bar magnets have a magnetic dipole moment of 1.0 Am2 each. They are kept in a plane in such a way that their axes are perpendicular to each other. A line drawn through the axis of one magnet passes through the center of other magnet. If the distance between their centers is 2 m, find the magnitude of the magnetic field at the midpoint of the line joining their centers.
A short bar magnet placed with its axis at 30° with a uniform external magnetic field of 0.25 T experiences a torque of magnitude equal to 4.5 × 10–2 J. What is the magnitude of magnetic moment of the magnet?
A closely wound solenoid of 2000 turns and area of cross-section 1.6 × 10–4 m2, carrying a current of 4.0 A, is suspended through its centre allowing it to turn in a horizontal plane.
- What is the magnetic moment associated with the solenoid?
- What is the force and torque on the solenoid if a uniform horizontal magnetic field of 7.5 × 10–2 T is set up at an angle of 30° with the axis of the solenoid?
If the bar magnet is turned around by 180°, where will the new null points be located?
Which of the following statements about bar magnet is correct?
Four point masses, each of value m, are placed at the comers of a square ABCD of side L, the moment of inertia of this system about an axis through A and parallel to BD is ______.
A ball of superconducting material is dipped in liquid nitrogen and placed near a bar magnet. (i) In which direction will it move? (ii) What will be the direction of it’s magnetic moment?
Use (i) the Ampere’s law for H and (ii) continuity of lines of B, to conclude that inside a bar magnet, (a) lines of H run from the N pole to S pole, while (b) lines of B must run from the S pole to N pole.
A long straight wire of circular cross section of radius 'a' carries a steady current I. The current is uniformly distributed across its cross section. The ratio of magnitudes of the magnetic field at a point `a/2` above the surface of wire to that of a point `a/2` below its surface is ______.
