Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
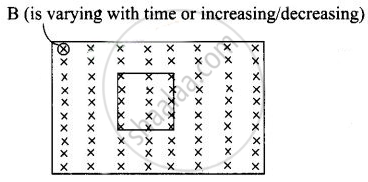
An e.m.f is produced in a coil, which is not connected to an external voltage source. This can be due to ______.
- the coil being in a time varying magnetic field.
- the coil moving in a time varying magnetic field.
- the coil moving in a constant magnetic field.
- the coil is stationary in external spatially varying magnetic field, which does not change with time.
विकल्प
a, c and d
a, b and d
b, c and d
a, b and c
उत्तर
a, b and c
Explanation:
As we know whenever the number of magnetic lines of force (magnetic flux) passing through a circuit changes, an emf is produced in the circuit called induced emf. The induced emf persists only as long as there is a change or cutting of flux.
In this problem, magnetic flux linked with the isolated coil changes when the coil is placed in the region of a time-varying magnetic field, the coil moving in a constant magnetic field or in time-varying magnetic field.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A conducting disc of radius r rotates with a small but constant angular velocity ω about its axis. A uniform magnetic field B exists parallel to the axis of rotation. Find the motional emf between the centre and the periphery of the disc.
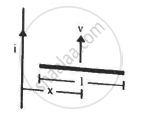
Figure shows a straight, long wire carrying a current i and a rod of length l coplanar with the wire and perpendicular to it. The rod moves with a constant velocity v in a direction parallel to the wire. The distance of the wire from the centre of the rod is x. Find the motional emf induced in the rod.
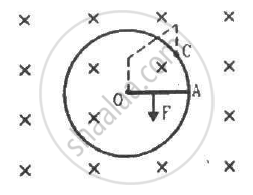
Consider the situation shown in the figure. Suppose the wire connecting O and C has zero resistance but the circular loop has a resistance Runiformly distributed along its length. The rod OA is made to rotate with a uniform angular speed ω as shown in the figure. Find the current in the rod when ∠ AOC = 90°.
A metal disc of radius 30 cm spins at 20 revolution per second about its transverse symmetry axis in a uniform magnetic field of 0.20 T. The field is parallel to the axis of rotation. Calculate
(a) the area swept out per second by the radius of the disc
(b) the flux cut per second by a radius of the disc
(c) the induced emf between the axle and rim of the disc.
Mechanical force per unit area of a charged conductor is ______
A cycle wheel of radius 0.6 m is rotated with constant angular velocity of 15 rad/s in a region of magnetic field of 0.2 T which is perpendicular to the plane of the wheel. The e.m.f generated between its center and the rim is, ____________.
A straight conductor of length 2 m moves in a uniform magnetic field of induction 2.5 x `10^-3` T with a velocity. of 4 m/s in a direction perpendicular to its length and also perpendicular to the field. The e.m.f. induced between the ends of the conductor is ______.
A wire of length 50 cm moves with a velocity of 300 m/min, perpendicular to a magnetic field. If the e.m.f. induced in the wire is 2 V, the magnitude of the field in tesla is ______.
Motional e.m.f is the induced e.m.f. ______
An aircraft of wing span of 60 m flies horizontally in earth’s magnetic field of 6 × 10−5 T at a speed of 500 m/s. Calculate the e.m.f. induced between the tips of the wings of the aircraft.
