Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A metal plate is getting heated. It can be because ______.
- a direct current is passing through the plate.
- it is placed in a time varying magnetic field.
- it is placed in a space varying magnetic field, but does not vary with time.
- a current (either direct or alternating) is passing through the plate.
विकल्प
a, b and d
a, c and d
b, c and d
a, b and c
उत्तर
a, b and d
Explanation:
When a changing magnetic flux is applied to a bulk piece of conducting material, then circulating currents called eddy currents are induced in the material. Because the resistance of the bulk conductor is usually low, eddy currents often have large magnitudes and heat up the conductor.
- These are circulating currents like eddies in water.
- The Experimental concept is given by Focault, hence also named as “Focault current”.
- The production of eddy currents in a metallic block leads to the loss of electric energy in the form of heat.
- By lamination and slotting processes, the resistance path for circulation of eddy current increases, resulting in weakening them and also reducing losses causes by them.
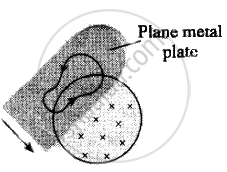
(A) Strong eddies produced cause excessive electro
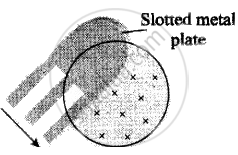
(B) Feeble eddies gradual damping
A metal plate is getting heated when a DC or AC current is passed through the plate, known as heating effect of current. This current (called eddy current) is induced in the plate when a metal plate is subjected to a time-varying magnetic field, i.e., the magnetic flux linked with the plate changes and eddy currents comes into existence which makes the plate hot.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write two examples of their useful applications .
How is Eddy current produced? How do they flow in a conductor?
Identify the wrong statement.
What are eddy currents?
A constant retarding force of50 N is applied to a body of mass 20 kg moving initially with a speed of 15 ms-1. How long does the body take to stop?
Two simple pendula of length L and 4L are pulled aside to the right and are at rest so that they make an angle 30° with the vertical. They are then released simultaneously at time t = 0. The time after which they will be in phase is ______.
For high frequency, capacity offers
Which one is not an application of eddy current?
Consider a metallic pipe with an inner radius of 1 cm. If a cylindrical bar magnet of radius 0.8 cm is dropped through the pipe, it takes more time to come down than it takes for a similar unmagnetised cylindrical iron bar dropped through the metallic pipe. Explain.
