Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An exterior angle of a cyclic quadrilateral is congruent to the angle opposite to its adjacent interior angle, to prove the theorem complete the activity.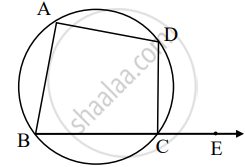
Given: ABCD is cyclic,
`square` is the exterior angle of ABCD
To prove: ∠DCE ≅ ∠BAD
Proof: `square` + ∠BCD = `square` .....[Angles in linear pair] (I)
ABCD is a cyclic.
`square` + ∠BAD = `square` ......[Theorem of cyclic quadrilateral] (II)
By (I) and (II)
∠DCE + ∠BCD = `square` + ∠BAD
∠DCE ≅ ∠BAD
योग
उत्तर
Proof:
Given: ABCD is cyclic,
∠DCE is the exterior angle of ABCD
To prove: ∠DCE ≅ ∠BAD
Proof: ∠DCE + ∠BCD = 180° .....[Angles in linear pair] (I)
ABCD is a cyclic.
∠BCD + ∠BAD = 180° ......[Theorem of cyclic quadrilateral] (II)
By (I) and (II)
∠DCE + ∠BCD = ∠BCD + ∠BAD
∠DCE ≅ ∠BAD
shaalaa.com
क्या इस प्रश्न या उत्तर में कोई त्रुटि है?
