Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer in brief.
On which factors does the wavelength of light emitted by a LED depend?
उत्तर
The intensity of the emitted light is proportional to the recombination rate and thus to the forward current of the diode. The colour of the light emitted by an LED is determined by the compound semiconductor material used as well as its composition (and doping levels), as shown below:
Typical semiconductor materials and emitted colours of LEDs
| Material | Emitted colour(s) |
| Gallium arsenide (GaAs), Indium gallium arsenide phosphide (InGaAsP) | Infrared |
| Aluminum gallium arsenide (AlGaAs) | Deep red, also IR laser |
| Indium gallium phosphide (InGaP) | Red |
| Gallium arsenide phosphide (GaAsP), aluminum indium gallium phosphide (AllnGaP) | Orange, red or yellow |
| Gallium phosphide (GaP) | Green or yellow |
| Aluminium gallium phosphide (AIGaP), zinc selenide (ZnSe), zinc selenide telluride (ZnSeTe), nitrogen impregnated gallium phosphide (GaP:N) | Green |
| Indium gallium nitride (InGaN), gallium nitride (GaN), sine sulphide (ZnS) | Blue and violet Longer wave lengths (green and yellow) are obtained by increasing the indium (In) content. Phosphor encapsulation produces white light. |
| Aluminium gallium nitride (AlGaN) | Ultraviolet |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Choose the correct option:
A Series resistance is connected in the Zener diode circuit to ______.
An LED emits visible light when it's ______.
Choose the correct option.
Solar cell operates on the principle of ______.
Answer in brief.
How is a Zener diode different than an ordinary diode?
Answer in brief.
Why should a photodiode be operated in reverse biased mode?
Answer in brief.
State the uses of the solar cell.
Explain how a Zener diode maintains a constant voltage across a load.
Explain the forward and the reverse characteristic of a Zener diode.
State any two advantages and disadvantages of a photodiode.
Define the dark current of the photodiode. What are the advantages and disadvantages of a photodiode?
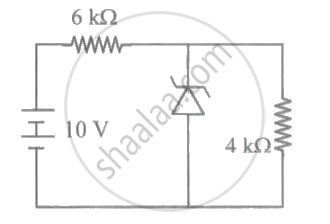
What will be the current flowing through the 6 kΩ resistor in the circuit shown, where the breakdown voltage of the Zener is 6V?
With a neat labelled diagram, explain the working of a photodiode. Calculate the wavelength in angstrom at which the emissive power is maximum for a blackbody heated to 3727 °C.
State the factors which control the wavelength of light emitte d by an LED.
Zener breakdown results from breaking of Si-Si covalent bonds in a silicon junction diode due to ______.
Give the name of the following symbol.
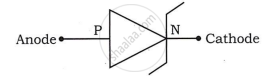
Draw a neat labelled schematic diagram of LED.
Distinguish between light-emitting diode and photo-diode.
What is a Light Emitting Diode?
Draw Light Emitting Diode circuit symbol.
