Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer the following question.
Explain the secondary structure of a protein with examples.
उत्तर
- There are two types of the secondary structures of protein: α-helix and β-pleated sheets.
- The polypeptide chain is arranged in a spiral helix. These spiral helices are of two types: α-helix (right-handed) and β-helix (left-handed).
- This spiral configuration is held together by hydrogen bonds.
- The sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain determines the location of its bend or fold and the position of formation of hydrogen bonds between different portions of the chain or between different chains. Thus, peptide chains form an α-helix structure.
- Example of α-helix structure is keratin.
- In some proteins two or more peptide chains are linked together by intermolecular hydrogen bonds. Such structures are called β-pleated sheets.
- Example of a β-pleated sheet is silk fibres.
- Due to the formation of hydrogen bonds peptide chains assume a secondary structure.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Answer the following question.
How many types of polysaccharides you know?
Answer the following question.
Enlist the significance of carbohydrates.
Answer the following question.
What is the basic difference between saturated and unsaturated fatty acid?
Answer the following with reference to the following figure.
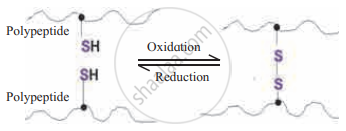
- Name the type of bond formed between two polypeptides.
- Which amino acid is involved in the formation of such bond?
- Amongst I, II, III and IV structural level of protein, which level of structure includes such bond?
Long answer question.
Explain the classes of carbohydrates with examples.
Long answer question.
Describe the types of lipids and mention their biological significance.
Long answer question.
Describe the models for enzyme actions.
If double-stranded DNA has 14% C (cytosine) what percent A (adenine), T (thymine) and G (gaunine) would you expect?
Name the form in which carbohydrate is transported in a plant.
Name the reagent used for testing for reducing sugar.
