Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Answer the following question.
Explain the secondary structure of a protein with examples.
Answer in Brief
Solution
- There are two types of the secondary structures of protein: α-helix and β-pleated sheets.
- The polypeptide chain is arranged in a spiral helix. These spiral helices are of two types: α-helix (right-handed) and β-helix (left-handed).
- This spiral configuration is held together by hydrogen bonds.
- The sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain determines the location of its bend or fold and the position of formation of hydrogen bonds between different portions of the chain or between different chains. Thus, peptide chains form an α-helix structure.
- Example of α-helix structure is keratin.
- In some proteins two or more peptide chains are linked together by intermolecular hydrogen bonds. Such structures are called β-pleated sheets.
- Example of a β-pleated sheet is silk fibres.
- Due to the formation of hydrogen bonds peptide chains assume a secondary structure.
shaalaa.com
Biomolecules in the Cell
Is there an error in this question or solution?
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain the peptide bond.
Answer the following question.
What is reducing sugar?
Answer the following question.
Explain the induced fit model for the mode of enzyme action.
Answer the following question.
What is RNA? Enlist types of RNA.
Answer the following question.
Describe the concept of metabolic pool.
Complete the following chart.
| Protein | Physiological role |
| Collagen | ___________ |
| __________ | Responsible for muscle contraction |
| Immunoglobulin IgG | ___________ |
| ___________ | Significant in respiration |
| Fibrinogen | ____________ |
Answer the following with reference to the following figure.
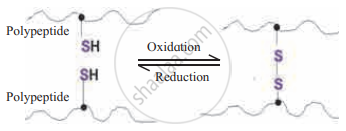
- Name the type of bond formed between two polypeptides.
- Which amino acid is involved in the formation of such bond?
- Amongst I, II, III and IV structural level of protein, which level of structure includes such bond?
Long answer question.
Describe the factors affecting enzyme action.
Name the term that describes all the chemical reactions taking place in an organism.
Name the reagent used for testing for reducing sugar.
