Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer the following question:
Which element of the first transition series has lowest enthalpy of atomisation?
उत्तर
Zinc is the element of the first transition series that has the lowest enthalpy of atomisation. The electronic configuration of zinc is: \[\ce{3d^10 4s^2}\]. This is because it has filled 3d-subshell and filled 4s-subshell so no unpaid electron is available for metallic bonding.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
How would you account for the following:
Of the d4 species, Cr2+ is strongly reducing while manganese (III) is strongly oxidising.
Following are the transition metal ions of 3d series:
Ti4+, V2+, Mn3+, Cr3+
(Atomic numbers: Ti = 22, V = 23, Mn = 25, Cr = 24)
Answer the following:
1) Which ion is most stable in an aqueous solution and why?
2) Which ion is a strong oxidising agent and why?
3) Which ion is colourless and why?
Read the passage given below and answer the following question:
The transition metals when exposed to oxygen at low and intermediate temperatures form thin, protective oxide films of up to some thousands of Angstroms in thickness. Transition metal oxides lie between the extremes of ionic and covalent binary compounds formed by elements from the left or right side of the periodic table. They range from metallic to semiconducting and deviate by both large and small degrees from stoichiometry. Since electron bonding levels are involved, the cations exist in various valence states and hence give rise to a large number of oxides. The crystal structures are often classified by considering a cubic or hexagonal close-packed lattice of one set of ions with the other set of ions filling the octahedral or tetrahedral interstices. The actual oxide structures, however, generally show departures from such regular arrays due in part to distortions caused by packing of ions of different size and to ligand field effects. These distortions depend not only on the number of d-electrons but also on the valence and the position of the transition metal in a period or group.
In the following questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices on the basis of the above passage.
Assertion: Transition metals form protective oxide films.
Reason: Oxides of transition metals are always stoichiometric.
When a chromite ore (A) is fused with sodium carbonate in free excess of air and the product is dissolved in water, a yellow solution of compound (B) is obtained. After treatment of this yellow solution with sulphuric acid, compound (C) can be crystallised from the solution. When compound (C) is treated with KCl, orange crystals of compound (D) crystallise out. Identify A to D and also explain the reactions.
When an oxide of manganese (A) is fused with KOH in the presence of an oxidising agent and dissolved in water, it gives a dark green solution of compound (B). Compound (B) disproportionates in neutral or acidic solution to give purple compound (C). An alkaline solution of compound (C) oxidises potassium iodide solution to a compound (D) and compound (A) is also formed. Identify compounds A to D and also explain the reactions involved.
On the basis of the figure given below, answer the following questions:
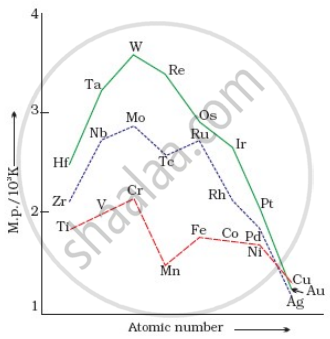
- Why Manganese has lower melting point than Chromium?
- Why do transition metals of 3d series have lower melting points as compared to 4d series?
- In the third transition series, identify and name the metal with the highest melting point.
Why is the `"E"_(("V"^(3+)//"V"^(2+)))^"o"` value for vanadium comparatively low?
Account for the following:
Eu2+ with electronic configuration [Xe]4f76s2 is a strong reducing agent.
Give two similarities in the properties of Sc and Zn.
Compare the general characteristics of the first series of the transition metals with those of the second and third series metals in the respective vertical columns. Give special emphasis on the following point:
Oxidation states
