Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How would you account for the following:
Of the d4 species, Cr2+ is strongly reducing while manganese (III) is strongly oxidising.
उत्तर
Both Cr2+ and Mn3+ have d4 electronic configurations, but their contrasting behaviors arise from the stability of their resulting oxidation states. Cr2+ is strongly reducing because it tends to lose one electron to form Cr3+ (d3 configuration). The d3 configuration has a half-filled t2g subshell in an octahedral field, which is particularly stable due to symmetric electron distribution and lower energy. On the other hand, Mn3+ is strongly oxidizing because it tends to gain one electron to form Mn2+ (d5 configuration). The d5 configuration corresponds to a half-filled d-subshell, which is highly stable due to exchange energy and symmetry. Thus, Cr2+ undergoes oxidation to achieve greater stability, while Mn3+ undergoes reduction for the same reason.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why +2 oxidation state of manganese is more stable?
What are the transition elements? Write two characteristics of the transition elements.
Account for the following:
Cu+ ion is unstable in aqueous solution.
In the series Sc (Z = 21) to Zn (Z = 30), the enthalpy of atomization of zinc is the lowest, i.e., 126 kJ mol−1. Why?
Why are Mn2+ compounds more stable than Fe2+ towards oxidation to their +3 state?
Which of the d-block elements may not be regarded as the transition elements?
For M2+/M and M3+/M2+ systems, the EΘ values for some metals are as follows:
| Cr2+/Cr | −0.9 V |
| Mn2+/Mn | −1.2 V |
| Fe2+/Fe | −0.4 V |
| Cr3/Cr2+ | −0.4 V |
| Mn3+/Mn2+ | +1.5 V |
| Fe3+/Fe2+ | +0.8 V |
Use this data to comment upon:
The stability of Fe3+ in acid solution as compared to that of Cr3+ or Mn3+.
Which metal in the first series of transition metals exhibits +1 oxidation state most frequently and why?
Write the formula of an oxo-anion of Chromium (Cr) in which it shows the oxidation state equal to its group number
How would you account for the following?
Transition metals and their compounds act as catalysts.
Although Zirconium belongs to 4d transition series and Hafnium to 5d transition series even then they show similar physical and chemical properties because ______.
Transition elements show high melting points. Why?
Identify A to E and also explain the reactions involved.
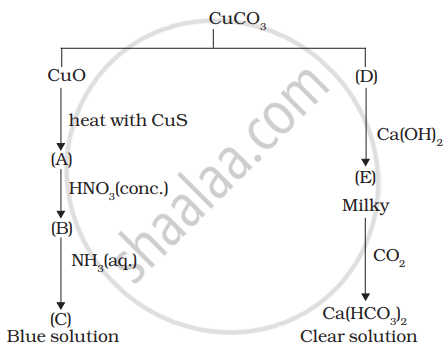
Passing H2S gas into a mixture of Mn2+ and Ni2+, Cu2+, ions in an acidified aqueous solution precipitates.
Match List - I with List - II.
| List - I | List - II | ||
| (a) | \[\ce{[Fe(CN)6]^3-}\] | (i) | 5.92 BM |
| (b) | \[\ce{[Fe(H2O)6]^3+}\] | (ii) | 0 BM |
| (c) | \[\ce{[Fe(CN)6]^4-}\] | (iii) | 4.90 BM |
| (d) | \[\ce{[Fe(H2O)6]^2+}\] | (iv) | 1.73 BM |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
Why are all copper halides known except that copper iodide?
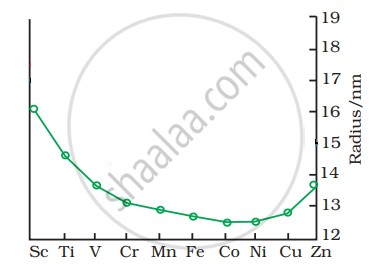
The trend of which property is represented by the following graph?
In order to protect iron from corrosion, which one will you prefer as a sacrificial electrode, Ni or Zn? Why? (Given standard electrode potentials of Ni, Fe and Zn are -0.25 V, -0.44 V and -0.76 V respectively.)
Describe the oxidising action of potassium dichromate and write the ionic equation for its reaction with H2S.
Compare the general characteristics of the first series of the transition metals with those of the second and third series metals in the respective vertical columns. Give special emphasis on the following point:
Ionisation enthalpies
