Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Why are Mn2+ compounds more stable than Fe2+ towards oxidation to their +3 state?
उत्तर
The electronic configuration of Mn2+ is [Ar]18 3d5 while that of Fe2+ is [Ar] 3d6. Since Mn2+ has a half-filled orbit (3d5), which is more stable than the 3d6 orbit of Fe2+, Mn2+ compounds are not easily oxidised to Mn3+ because of very high second ionization enthalpy. In contrast, Fe2+ compounds are easily oxidised to Fe3+ due to lower second ionization enthalpy. This is the reason that Mn2+ compounds are more stable than Fe2+ towards oxidation to their +3 state.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Account for the following:
Cu+2 salts are coloured, while Zn2+ salts are white.
Account for the following:
E° value for the Mn3+/Mn2+ couple is much more positive than that for Cr3+/Cr2+.
Which of the 3d series of the transition metals exhibits the largest number of oxidation states and why?
Why is the highest oxidation state of a metal exhibited in its oxide or fluoride only?
Which is the most stable oxidation state of iron?
Why EΘ values for Mn, Ni and Zn are more negative than expected?
When a brown compound of manganese (A) is treated with \[\ce{HCl}\] it gives a gas (B). The gas taken in excess, reacts with \[\ce{NH3}\] to give an explosive compound (C). Identify compounds A, B and C.
Answer the following question:
Which element of the first transition series has highest second ionisation enthalpy?
Identify the metal and justify your answer.
Carbonyl \[\ce{M(CO)5}\]
Identify the metal and justify your answer.
\[\ce{MO3F}\]
Transition metals can act as catalysts because these can change their oxidation state. How does \[\ce{Fe(III)}\] catalyse the reaction between iodide and persulphate ions?
A violet compound of manganese (A) decomposes on heating to liberate oxygen and compounds (B) and (C) of manganese are formed. Compound (C) reacts with KOH in the presence of potassium nitrate to give compound (B). On heating compound (C) with conc. \[\ce{H2SO4}\] and \[\ce{NaCl}\], chlorine gas is liberated and a compound (D) of manganese along with other products is formed. Identify compounds A to D and also explain the reactions involved.
Fill in the blanks by choosing the appropriate word(s) from those given in the brackets:
(activation energy, Threshold energy, increased, lowered, partially, full, d-d transition, Benzoic acid, benzaldehyde)
Only those transition metal ions will be coloured which have ______ filled d-orbitals facilitating ______.
On the basis of the figure given below, answer the following questions:
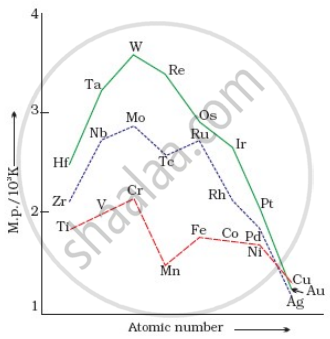
- Why Manganese has lower melting point than Chromium?
- Why do transition metals of 3d series have lower melting points as compared to 4d series?
- In the third transition series, identify and name the metal with the highest melting point.
The element with atomic number 53 belongs to
A complex in which dsp2 hybridisation takes place is
How is the variability in oxidation states of transition metals different from that of p-block elements?
A pair of coloured ions is ______.
Explain the use of different transition metals as catalysts.
