Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer the following question.
Write three points of differences between para-, dia- and ferromagnetic materials, giving one example for each.
उत्तर
Ferromagnetism:
These substances are strongly attracted by a magnetic field. Ferromagnetic substances can be permanently magnetized even in the absence of a magnetic field. These substances move (strongly) towards the strong field region when kept a non-uniform external magnetic field. Some examples of ferromagnetic substances are iron, cobalt, nickel, gadolinium
Paramagnetism:
The substances that are attracted by a magnetic field are called paramagnetic substances. These substances get magnetized in a magnetic field in the same direction but lose magnetism when the magnetic field is removed. Paramagnetic material moves (weakly) towards the weak field region when kept a non-uniform external magnetic field. To undergo paramagnetism, a substance must have one or more unpaired electrons.
Example O2
Diamagnetism:
This is a form of magnetism that is only exhibited by a substance in the presence of an externally applied magnetic field. It is generally quite a weak effect in most materials, although superconductors exhibit a strong effect. Diamagnetic material moves (very weakly) away from the strong-field region towards the weak field region. Diamagnetic atoms have only paired electrons. Example H2
संबंधित प्रश्न
The susceptibility of a magnetic material is − 2.6 × 10−5. Identify the type of magnetic material and state its two properties.
A rod of magnetic material of cross-section 0.25 cm2 is placed in a magnetizing field of intensity 4000 A/m-1. The magnetic flux passing through the rod is 25 × 10-6 Wb. Find out
(a) relative permeability
(b) magnetic susceptibility and
(c) magnetisation of the rod.
Above the curie temperature the susceptibility of ferromagnetic substance varies ____________.
If a toroid uses bismuth for its core, will the field in the core be (slightly) greater or (slightly) less than when the core is empty?
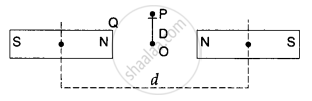
Two identical bar magnets are fixed with their centres at a distance d apart. A stationary charge Q is placed at P in between the gap of the two magnets at a distance D from the centre O as shown in the figure. The force on the charge Q is ______.
A hydrogen atom is paramagnetic. A hydrogen molecule is
A long solenoid has 1000 turns per metre and carries a current of 1 A. It has a soft iron core of µr = 1000. The core is heated beyond the Curie temperature, Tc.
- The H field in the solenoid is (nearly) unchanged but the B field decreases drastically.
- The H and B fields in the solenoid are nearly unchanged.
- The magnetisation in the core reverses direction.
- The magnetisation in the core diminishes by a factor of about 108.
Explain ferromagnetism on the basis of the domain theory.
Explain the meaning of the following statement:
Curie temperature for soft iron is 770°C.
