Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain ferromagnetism on the basis of the domain theory.
Explain ferromagnetism with the help of suitable diagrams, using the concept of magnetic domain.
उत्तर १
Due mostly to the electrons' spin magnetic moments, ferromagnetic material atoms have a persistent non-zero magnetic dipole moment. Little areas known as domains make up a ferromagnetic substance, according to the domain hypothesis. An incredibly small area with a high concentration of atoms—roughly 1015 atoms, or the same number as ordinary iron—is called a domain. Even in the absence of an external magnetic field, the atomic magnetic moments of nearest-neighbour atoms within each domain interact strongly through exchange interaction, a phenomenon described by quantum mechanics. As a result, the atoms align themselves parallel to one another. That is, a domain becomes spontaneously magnetised to saturation. In an unsealed substance, on the other hand, the net magnetisation is zero due to the distinct domains' magnetisation orientations being so aligned.

Domains in a single crystal of iron The arrows indicate the direction and magnitude of the magnetization of each domain.
The specimen becomes more magnetised as a result of applying an external magnetic field. One of two methods is used to do this: either a favourably oriented domain expands at the expense of a less favourably oriented domain, or the magnetisation direction of an entire domain shifts to align with the external magnetic field. Favourably oriented domains increase in size by domain border displacement when a weak magnetic field is applied, as shown in Fig. (b). Figs. (c) and (d) show how domain rotation causes the domains to shift their magnetisation under strong fields. When domains line perfectly, as they do in Fig. (d), they combine to form a single, huge domain.
It might be energetically advantageous for a domain's direction of magnetisation to continue after the external field is eliminated. A persistent magnetic dipole moment is thus present in the specimen. The existence of permanent magnets is based on a phenomenon known as magnetic remanence.
उत्तर २
Ferromagnetism based on domain theory:
- Individual atoms in ferromagnetic materials are linked to significant magnetic moments.
- The magnetic moments of atoms close to each other interact and naturally line up in the same way over large areas known as domains.
- Each domain typically measures approximately 1 mm and comprises around 1011 atoms. So, each domain possesses a significant magnetic moment.
- Without an external magnetic field, these domains are arbitrarily oriented, resulting in a net magnetic moment of zero.
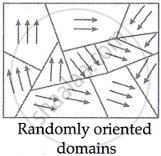
- When subjected to a magnetic field, all of the domains align with one another along the direction of the field being applied.
- Magnets aggressively attract ferromagnetic materials.
- The alignment of domains may occur in either of the two ways.
- By displacing the boundaries of domains.
- By rotation of domains.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Which of the following substances is ductile?
Give any ‘two’ points of differences between diamagnetic and ferromagnetic substances.
The susceptibility of magnesium at 200 K is 1.8 x 10-5. At what temperature will the susceptibility decrease by 6 x 10-6?
Out of the two magnetic materials, 'A' has relative permeability slightly greater than unity while 'B' has less than unity. Identify the nature of the materials 'A' and 'B'. Will their susceptibilities be positive or negative?
Distinguish between diamagnetic and paramagnetic substances
The magnetic susceptibility of annealed iron at saturation is 4224. Find the permeability of
annealed iron at saturation. (μ0 = 4Π × 10−7 SI unit)
Explain Curie’s law for a paramagnetic substance.
The relative magnetic permeability of a magnetic material is 800. Identify the nature of magnetic material and state its two properties.
Draw magnetic field line when a (i) diamagnetic, (ii) paramagnetic substance is placed in an external magnetic field. Which magnetic property distinguishes this behaviour of the field line due to the substances?
A tangent galvanometer shows a deflection of 45° when 10 mA of current is passed through it. If the horizontal component of the earth's magnetic field is `B_H = 3.6 xx 10^-5 "T"` and radius of the coil is 10 cm, find the number of turns in the coil.
Answer the following question.
Write three points of differences between para-, dia- and ferromagnetic materials, giving one example for each.
Which of the following statements is correct for diamagnetic materials?
Choose the correct option:
A rectangular magnet suspended freely has a period of oscillation equal to T. Now it is broken into two equal halves (each having half of the original length) and one piece is made to oscillate freely. Its period of oscillation is T′, the ratio of T′/T is ______.
Answer in brief.
Discuss the Curie law for paramagnetic material.
A paramagnetic gas has 2.0 × 1026 atoms/m with atomic magnetic dipole moment of 1.5 × 10−23 A m2 each. The gas is at 27°C.
- Find the maximum magnetization intensity of this sample.
- If the gas in this problem is kept in a uniform magnetic field of 3 T, is it possible to achieve saturation magnetization? Why?
Two identical bar magnets each of magnetic moment M, separated by some distance are kept perpendicular to each other. The magnetic induction at a point at the same distance d from the centre of magnets, is (µ0 = permeability of free space)
For a paramagnetic substance, the magnetic susceptibility is ______.
The susceptibility of a magnetic material is positive and small. The material is ______.
If a magnetic field is applied to a liquid in one arm of a narrow U-tube, the liquid level in that arm is lowered. The liquid in U-tube arm is ______.
Relative permittivity and permeability of a material are `epsilon_"r"` and `µ_"r"` respectively. Which of the following values of these quantities are allowed for a diamagnetic material?
A domain in a ferromagnetic substance is in the form of a cube of side length 1 µm. If it contains 6 x 1010 atoms and each atomic dipole has a dipole moment of 7 x 10-24 Am2, then magnetization of the domain is ____________.
The earth’s field departs from its dipole shape substantially at large distances (greater than about 30,000 km). What agencies may be responsible for this distortion?
Why is diamagnetism, in contrast, almost independent of temperature?
If a toroid uses bismuth for its core, will the field in the core be (slightly) greater or (slightly) less than when the core is empty?
Magnetic field lines are always nearly normal to the surface of a ferromagnet at every point. (This fact is analogous to the static electric field lines being normal to the surface of a conductor at every point.) Why?
Would the maximum possible magnetisation of a paramagnetic sample be of the same order of magnitude as the magnetisation of a ferromagnet?
Explain qualitatively on the basis of domain picture the irreversibility in the magnetisation curve of a ferromagnet.
Nickel shows ferromagnetic property at room temperature. If the temperature is increased beyond curie temperature, then it will show ______.
Assertion: The ferromagnetic substance do not obey Curie’s law.
Reason: At Curie point a ferromagnetic substance start behaving as a paramagnetic substance.
Metals getting magnetised by orientation of atomic magnetic moments in external magnetic field are called ______.
Which of the following property shows the property of ferromagnetic substances?
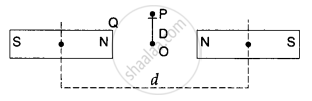
Two identical bar magnets are fixed with their centres at a distance d apart. A stationary charge Q is placed at P in between the gap of the two magnets at a distance D from the centre O as shown in the figure. The force on the charge Q is ______.
When a ferromagnetic material is created above its curie temperature
A hydrogen atom is paramagnetic. A hydrogen molecule is
For a diamagnetic material
Most of the substance show which of the magnetic property:-
According to the Atomic theory, on heating a magnet, the thermal energy of the elementary magnet ______
S is the surface of a lump of magnetic material.
- Lines of B are necessarily continuous across S.
- Some lines of B must be discontinuous across S.
- Lines of H are necessarily continuous across S.
- Lines of H cannot all be continuous across S.
A permanent magnet in the shape of a thin cylinder of length 10 cm has M = 106 A/m. Calculate the magnetisation current IM.
From molecular view point, discuss the temperature dependence of susceptibility for diamagnetism, paramagnetism and ferromagnetism.
If the magnetizing field on a ferromagnetic material is increased, its permeability ______.
- Assertion (A): Diamagnetic substances exhibit magnetism.
- Reason (R): Diamagnetic materials do not have a permanent magnetic dipole moment.
Which of the following has a permeability less than that of free space?
What is magnetic hysterisis?
Explain the Domain theory in brief.
Explain the meaning of the following statement:
Curie temperature for soft iron is 770°C.
Magnetic susceptibility of a diamagnetic substance ______.
