Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The susceptibility of magnesium at 200 K is 1.8 x 10-5. At what temperature will the susceptibility decrease by 6 x 10-6?
उत्तर
Given,
T = 200K,
χ1 = 1.8 × 10−5
χ1 - χ2 = 6 × 10-6
To Find: Required temperature (T2)
Formula: χT=constatnt
Calculation :
χ1 - χ2 = 6 × 10-6
χ2 = 1.8×10-5 - 0.6×10-5
χ2 = 1.2 ×10-5
From formula,
∴χT = constant
χ1T1 = χ2T2
`T_2 =(chi_1T_1)/chi_2`
`T_2=(1.8xx10^-5xx200)/(1.2xx10^-5)`
`T_2 = 300K `
The required temperature is 300 K.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Distinguish between ‘paramagnetic’ and ‘ferromagnetic’ substances.
Give any ‘two’ points of differences between diamagnetic and ferromagnetic substances.
In what way is the behaviour of a diamagnetic material different from that of a paramagnetic, when kept in an external magnetic field?
A meter gauge train is heading north with speed 54 km/hr in earth's magnetic field 3 x 10-4T. The e.m.f. induced across the axle joining the wheels is ..........
(a) 0.45 mV
(b) 4.5 mV
(c) 45 mV
(d) 450 m V
The magnetic susceptibility of annealed iron at saturation is 4224. Find the permeability of
annealed iron at saturation. (μ0 = 4Π × 10−7 SI unit)
The susceptibility of a magnetic material is 0·9853. Identify the type of magnetic material. Draw the modification of the field pattern on keeping a piece of this material in a uniform magnetic field.
Which of the following substances are diamagnetic?
Bi, Al, Na, Cu, Ca and Ni
A tangent galvanometer shows a deflection of 45° when 10 mA of current is passed through it. If the horizontal component of the earth's magnetic field is `B_H = 3.6 xx 10^-5 "T"` and radius of the coil is 10 cm, find the number of turns in the coil.
The magnetic susceptibility of platinum is 0.0001. It's relative permeability is:
Answer the following question.
Write three points of differences between para-, dia- and ferromagnetic materials, giving one example for each.
Identify the following magnetic materials :
Choose the correct option:
A magnetising field of 360 Am−1 produces a magnetic flux density (B) = 0.6T in a ferromagnetic material. What is its permeability in Tm A−1?
What happens to a ferromagnetic material when its temperature increases above curie temperature?
The susceptibility of a paramagnetic material is χ at 27° C. At what temperature its susceptibility be χ/3?
A rod of magnetic material of cross-section 0.25 cm2 is placed in a magnetizing field of intensity 4000 A/m-1. The magnetic flux passing through the rod is 25 × 10-6 Wb. Find out
(a) relative permeability
(b) magnetic susceptibility and
(c) magnetisation of the rod.
Two identical bar magnets each of magnetic moment M, separated by some distance are kept perpendicular to each other. The magnetic induction at a point at the same distance d from the centre of magnets, is (µ0 = permeability of free space)
The magnetic susceptibility of a paramagnetic material at - 73 °C is 0.0075. Its value at -173 °C will be ______.
All atoms of a magnetic substance have a resultant magnetic moment even in absence of external magnetic field. The substance is ______.
If a magnetic field is applied to a liquid in one arm of a narrow U-tube, the liquid level in that arm is lowered. The liquid in U-tube arm is ______.
The materials having negative magnetic susceptibility are ____________.
The magnetic property of magnetic substance is associated with ____________.
Above the curie temperature the susceptibility of ferromagnetic substance varies ____________.
A sphere of gold when brought towards a powerful magnet experiences ____________.
A small quantity of paramagnetic liquid is taken in a watch - glass and kept on two dissimilar magnetic poles. The liquid ____________.
Why is diamagnetism, in contrast, almost independent of temperature?
Explain qualitatively on the basis of domain picture the irreversibility in the magnetisation curve of a ferromagnet.
What kind of ferromagnetic material is used for coating magnetic tapes in a cassette player, or for building ‘memory stores’ in a modern computer?
A certain region of space is to be shielded from magnetic fields. Suggest a method.
The given figure represents a material which is ______.
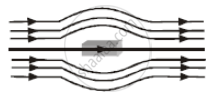
Assertion: A paramagnetic sample display greater magnetisation (for the same magnetic field) when cooled.
Reason: The magnetisation does not depend on temperature.
The magnetic susceptibility is negative for ______.
Which of the following property shows the property of ferromagnetic substances?
Earth's magnetic field analyses has a horizontal component except at:-
For a diamagnetic material
A paramagnetic sample shows a net magnetisation of 8 Am–1 when placed in an external magnetic field of 0.6 T at a temperature of 4 K. When the same sample is placed in an external magnetic field of 0.2 T at a temperature of 16 K, the magnetisation will be ______.
A long solenoid has 1000 turns per metre and carries a current of 1 A. It has a soft iron core of µr = 1000. The core is heated beyond the Curie temperature, Tc.
- The H field in the solenoid is (nearly) unchanged but the B field decreases drastically.
- The H and B fields in the solenoid are nearly unchanged.
- The magnetisation in the core reverses direction.
- The magnetisation in the core diminishes by a factor of about 108.
A permanent magnet in the shape of a thin cylinder of length 10 cm has M = 106 A/m. Calculate the magnetisation current IM.
From molecular view point, discuss the temperature dependence of susceptibility for diamagnetism, paramagnetism and ferromagnetism.
If the magnetizing field on a ferromagnetic material is increased, its permeability ______.
A uniform magnetic field gets modified as shown in figure when two specimens A and B are placed in it.
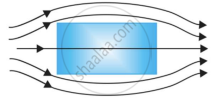 |
 |
| (a) | (b) |
- Identify the specimen A and B.
- How is the magnetic susceptibility of specimen A different from that of specimen B?
Magnetic susceptibility for a paramagnetic and diamagnetic materials is respectively ______.
- Assertion (A): Diamagnetic substances exhibit magnetism.
- Reason (R): Diamagnetic materials do not have a permanent magnetic dipole moment.
Which of the following has a permeability less than that of free space?
Which of the following cannot modify an external magnetic field as shown in the figure?

What is magnetic hysterisis?
