Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The susceptibility of a paramagnetic material is χ at 27° C. At what temperature its susceptibility be χ/3?
उत्तर
Data: χm1 = χ, T1 = 27°C = 300 K, χm2 = `χ/3`
By Curie's law,
`"M"_"z" = "C" "B"_0/"T"`
Since Mz = χmH and B0 = μ0H
χmH = C`(mu_0"H")/"T"`
∴ χm = C `mu_0/"T"`
∴ χm ∝ `1/"T"`
∴ `(chi_"m1")/(chi_"m2") = "T"_2/"T"_1`
∴ `"T"_2 = (chi_"m1")/(chi_"m2") xx "T"_1 = 3 chi/chi xx 300 = 900 "K" = 627^circ "C"`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Which of the following substances is ductile?
Give any ‘two’ points of differences between diamagnetic and ferromagnetic substances.
The susceptibility of magnesium at 200 K is 1.8 x 10-5. At what temperature will the susceptibility decrease by 6 x 10-6?
Out of the two magnetic materials, 'A' has relative permeability slightly greater than unity while 'B' has less than unity. Identify the nature of the materials 'A' and 'B'. Will their susceptibilities be positive or negative?
Show diagrammatically the behaviour of magnetic field lines in the presence of (i) paramagnetic and (ii) diamagnetic substances. How does one explain this distinguishing feature?
Distinguish between diamagnetic and paramagnetic substances
The magnetic susceptibility of annealed iron at saturation is 4224. Find the permeability of
annealed iron at saturation. (μ0 = 4Π × 10−7 SI unit)
The susceptibility of a magnetic material is 0·9853. Identify the type of magnetic material. Draw the modification of the field pattern on keeping a piece of this material in a uniform magnetic field.
Explain Curie’s law for a paramagnetic substance.
Which of the following substances are para-magnetic?
Bi, Al, Cu, Ca, Pb, Ni
The susceptibility of a magnetic material is − 2.6 × 10−5. Identify the type of magnetic material and state its two properties.
The relative magnetic permeability of a magnetic material is 800. Identify the nature of magnetic material and state its two properties.
Draw magnetic field line when a (i) diamagnetic, (ii) paramagnetic substance is placed in an external magnetic field. Which magnetic property distinguishes this behaviour of the field line due to the substances?
The magnetic susceptibility of platinum is 0.0001. It's relative permeability is:
Two substances A and B have their relative permeability slightly greater and slightly less than 1 respectively. What do you conclude about A and B as far as their magnetic materials are concerned?
Answer the following question.
Write three points of differences between para-, dia- and ferromagnetic materials, giving one example for each.
Which of the following statements is correct for diamagnetic materials?
Choose the correct option:
A rectangular magnet suspended freely has a period of oscillation equal to T. Now it is broken into two equal halves (each having half of the original length) and one piece is made to oscillate freely. Its period of oscillation is T′, the ratio of T′/T is ______.
Choose the correct option:
A magnetising field of 360 Am−1 produces a magnetic flux density (B) = 0.6T in a ferromagnetic material. What is its permeability in Tm A−1?
A paramagnetic gas has 2.0 × 1026 atoms/m with atomic magnetic dipole moment of 1.5 × 10−23 A m2 each. The gas is at 27°C.
- Find the maximum magnetization intensity of this sample.
- If the gas in this problem is kept in a uniform magnetic field of 3 T, is it possible to achieve saturation magnetization? Why?
A rod of magnetic material of cross-section 0.25 cm2 is placed in a magnetizing field of intensity 4000 A/m-1. The magnetic flux passing through the rod is 25 × 10-6 Wb. Find out
(a) relative permeability
(b) magnetic susceptibility and
(c) magnetisation of the rod.
A domain in a ferromagnetic substance is in the form of a cube of side 1 µm. If it contains 8 × 1010 atoms and each atomic dipole has a dipole moment of 9 × 10-24 Am2 then the magnetisation of the domain is ______.
For a paramagnetic substance, the magnetic susceptibility is ______.
The susceptibility of a magnetic material is positive and small. The material is ______.
Magnetization of the sample is ______.
Magnetic material can be easily magnetized if magnetic susceptibility is ______.
If a magnetic field is applied to a liquid in one arm of a narrow U-tube, the liquid level in that arm is lowered. The liquid in U-tube arm is ______.
Relative permittivity and permeability of a material are `epsilon_"r"` and `µ_"r"` respectively. Which of the following values of these quantities are allowed for a diamagnetic material?
Would the maximum possible magnetisation of a paramagnetic sample be of the same order of magnitude as the magnetisation of a ferromagnet?
Explain qualitatively on the basis of domain picture the irreversibility in the magnetisation curve of a ferromagnet.
The given figure represents a material which is ______.
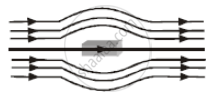
Which of the following property shows the property of ferromagnetic substances?
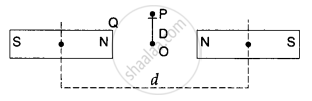
Two identical bar magnets are fixed with their centres at a distance d apart. A stationary charge Q is placed at P in between the gap of the two magnets at a distance D from the centre O as shown in the figure. The force on the charge Q is ______.
Earth's magnetic field analyses has a horizontal component except at:-
A hydrogen atom is paramagnetic. A hydrogen molecule is
The universal property of all substances is ______.
According to the Atomic theory, on heating a magnet, the thermal energy of the elementary magnet ______
Essential difference between electrostatic shielding by a conducting shell and magnetostatic shielding is due to ______.
- electrostatic field lines can end on charges and conductors have free charges.
- lines of B can also end but conductors cannot end them.
- lines of B cannot end on any material and perfect shielding is not possible.
- shells of high permeability materials can be used to divert lines of B from the interior region.
A permanent magnet in the shape of a thin cylinder of length 10 cm has M = 106 A/m. Calculate the magnetisation current IM.
If the magnetizing field on a ferromagnetic material is increased, its permeability ______.
A uniform magnetic field gets modified as shown in figure when two specimens A and B are placed in it.
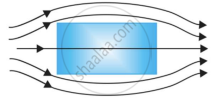 |
 |
| (a) | (b) |
- Identify the specimen A and B.
- How is the magnetic susceptibility of specimen A different from that of specimen B?
- Assertion (A): Diamagnetic substances exhibit magnetism.
- Reason (R): Diamagnetic materials do not have a permanent magnetic dipole moment.
Which of the following cannot modify an external magnetic field as shown in the figure?

Explain ferromagnetism on the basis of the domain theory.
Explain the Domain theory in brief.
