Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A paramagnetic gas has 2.0 × 1026 atoms/m with atomic magnetic dipole moment of 1.5 × 10−23 A m2 each. The gas is at 27°C.
- Find the maximum magnetization intensity of this sample.
- If the gas in this problem is kept in a uniform magnetic field of 3 T, is it possible to achieve saturation magnetization? Why?
उत्तर
Data: `"N"/"V" = 2.0 xx 10^26` atoms/m3,
µ = 1.5 × 10-23 Am2, T = 27 + 273 = 300 K, B = 3 T, kB = 1.38 × 10-23 J/K, 1 eV = 1.6 × 10-19 J
(a) The maximum magnetization of the material,
`"M"_"z" = "N"/"V" mu = (2.0 xx 10^26)(1.5 xx 10^-23)`
= 3 × 103 A/m
(b) The maximum orientation energy per atom is
`upsilon_"max" = - mu"B" cos 180^circ = mu"B"`
`= (1.5 xx 10^-23)(3) = (4.5 xx 10^-23)/(1.6 xx 10^-19)`
= 2.8 × 10-4 eV
The average thermal energy of each atom,
E = `3/2 "k"_"B" "T"`
where kB is the Botzmann constant.
∴ E = 1.5(1.38 × 10-23)(300)
= 6.21 × 10-21 J = `(6.21 xx 10^-21)/(1.6 xx 10^-19)`
= 3.9 × 10-2 eV
Since the thermal energy of randomization is about two orders of magnitude greater than the magnetic potential energy of orientation, saturation magnetization will not be achieved at 300 K.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Distinguish between ‘paramagnetic’ and ‘ferromagnetic’ substances.
Which of the following substances is ductile?
Give any ‘two’ points of differences between diamagnetic and ferromagnetic substances.
The susceptibility of magnesium at 200 K is 1.8 x 10-5. At what temperature will the susceptibility decrease by 6 x 10-6?
A meter gauge train is heading north with speed 54 km/hr in earth's magnetic field 3 x 10-4T. The e.m.f. induced across the axle joining the wheels is ..........
(a) 0.45 mV
(b) 4.5 mV
(c) 45 mV
(d) 450 m V
Which of the following substances are diamagnetic?
Bi, Al, Na, Cu, Ca and Ni
Draw magnetic field line when a (i) diamagnetic, (ii) paramagnetic substance is placed in an external magnetic field. Which magnetic property distinguishes this behaviour of the field line due to the substances?
The magnetic susceptibility of platinum is 0.0001. It's relative permeability is:
Two substances A and B have their relative permeability slightly greater and slightly less than 1 respectively. What do you conclude about A and B as far as their magnetic materials are concerned?
Answer the following question.
Write three points of differences between para-, dia- and ferromagnetic materials, giving one example for each.
What happens to a ferromagnetic material when its temperature increases above curie temperature?
A domain in a ferromagnetic substance is in the form of a cube of side 1 µm. If it contains 8 × 1010 atoms and each atomic dipole has a dipole moment of 9 × 10-24 Am2 then the magnetisation of the domain is ______.
All atoms of a magnetic substance have a resultant magnetic moment even in absence of external magnetic field. The substance is ______.
Magnetic material can be easily magnetized if magnetic susceptibility is ______.
If a magnetic field is applied to a liquid in one arm of a narrow U-tube, the liquid level in that arm is lowered. The liquid in U-tube arm is ______.
There are three needles 'N1', 'N2' and 'N3' made of a ferromagnetic, a paramagnetic and a diamagnetic substance respectively. When a magnet is brought close to them, then it will ____________.
The materials having negative magnetic susceptibility are ____________.
A domain in a ferromagnetic substance is in the form of a cube of side length 1 µm. If it contains 6 x 1010 atoms and each atomic dipole has a dipole moment of 7 x 10-24 Am2, then magnetization of the domain is ____________.
Why does a paramagnetic sample display greater magnetisation (for the same magnetising field) when cooled?
Is the permeability of a ferromagnetic material independent of the magnetic field? If not, is it more for lower or higher fields?
Magnetic field lines are always nearly normal to the surface of a ferromagnet at every point. (This fact is analogous to the static electric field lines being normal to the surface of a conductor at every point.) Why?
A certain region of space is to be shielded from magnetic fields. Suggest a method.
Nickel shows ferromagnetic property at room temperature. If the temperature is increased beyond curie temperature, then it will show ______.
The given figure represents a material which is ______.
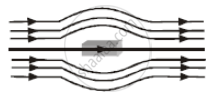
Which of the following property shows the property of ferromagnetic substances?
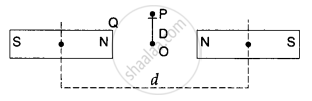
Two identical bar magnets are fixed with their centres at a distance d apart. A stationary charge Q is placed at P in between the gap of the two magnets at a distance D from the centre O as shown in the figure. The force on the charge Q is ______.
The magnetic susceptibility for diamagnetic materials is ______.
When a ferromagnetic material is created above its curie temperature
A hydrogen atom is paramagnetic. A hydrogen molecule is
Most of the substance show which of the magnetic property:-
S is the surface of a lump of magnetic material.
- Lines of B are necessarily continuous across S.
- Some lines of B must be discontinuous across S.
- Lines of H are necessarily continuous across S.
- Lines of H cannot all be continuous across S.
A long solenoid has 1000 turns per metre and carries a current of 1 A. It has a soft iron core of µr = 1000. The core is heated beyond the Curie temperature, Tc.
- The H field in the solenoid is (nearly) unchanged but the B field decreases drastically.
- The H and B fields in the solenoid are nearly unchanged.
- The magnetisation in the core reverses direction.
- The magnetisation in the core diminishes by a factor of about 108.
Explain quantitatively the order of magnitude difference between the diamagnetic susceptibility of N2 (~5 × 10–9) (at STP) and Cu (~10–5).
From molecular view point, discuss the temperature dependence of susceptibility for diamagnetism, paramagnetism and ferromagnetism.
A uniform magnetic field gets modified as shown in figure when two specimens A and B are placed in it.
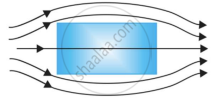 |
 |
| (a) | (b) |
- Identify the specimen A and B.
- How is the magnetic susceptibility of specimen A different from that of specimen B?
Magnetic susceptibility for a paramagnetic and diamagnetic materials is respectively ______.
An ammeter of resistance R gives a full-scale deflection when a current of 2 A passes through it. If it is measured with a maximum current of 10 A, the required shunt is ______.
- Assertion (A): Diamagnetic substances exhibit magnetism.
- Reason (R): Diamagnetic materials do not have a permanent magnetic dipole moment.
The relative magnetic permeability of a substance X is slightly less than unity and that of substance Y is slightly more than unity, then ______.
Explain the origin of paramagnetism on the basis of atomic structure.
Explain the Domain theory in brief.
Explain the meaning of the following statement:
Curie temperature for soft iron is 770°C.
Magnetic susceptibility of a diamagnetic substance ______.
