Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The susceptibility of magnesium at 200 K is 1.8 x 10-5. At what temperature will the susceptibility decrease by 6 x 10-6?
Solution
Given,
T = 200K,
χ1 = 1.8 × 10−5
χ1 - χ2 = 6 × 10-6
To Find: Required temperature (T2)
Formula: χT=constatnt
Calculation :
χ1 - χ2 = 6 × 10-6
χ2 = 1.8×10-5 - 0.6×10-5
χ2 = 1.2 ×10-5
From formula,
∴χT = constant
χ1T1 = χ2T2
`T_2 =(chi_1T_1)/chi_2`
`T_2=(1.8xx10^-5xx200)/(1.2xx10^-5)`
`T_2 = 300K `
The required temperature is 300 K.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Distinguish between ‘paramagnetic’ and ‘ferromagnetic’ substances.
Give any ‘two’ points of differences between diamagnetic and ferromagnetic substances.
An iron rod of the area of cross-section 0.1m2 is subjected to a magnetizing field of 1000 A/m. Calculate the magnetic permeability of the iron rod. [Magnetic susceptibility of iron = 59.9, magnetic permeability of vacuum = 4π x 10-7 S. I. unit]
In what way is the behaviour of a diamagnetic material different from that of a paramagnetic, when kept in an external magnetic field?
Show diagrammatically the behaviour of magnetic field lines in the presence of (i) paramagnetic and (ii) diamagnetic substances. How does one explain this distinguishing feature?
A meter gauge train is heading north with speed 54 km/hr in earth's magnetic field 3 x 10-4T. The e.m.f. induced across the axle joining the wheels is ..........
(a) 0.45 mV
(b) 4.5 mV
(c) 45 mV
(d) 450 m V
The magnetic susceptibility of annealed iron at saturation is 4224. Find the permeability of
annealed iron at saturation. (μ0 = 4Π × 10−7 SI unit)
The susceptibility of a magnetic material is 0·9853. Identify the type of magnetic material. Draw the modification of the field pattern on keeping a piece of this material in a uniform magnetic field.
Explain Curie’s law for a paramagnetic substance.
The relative magnetic permeability of a magnetic material is 800. Identify the nature of magnetic material and state its two properties.
A tangent galvanometer shows a deflection of 45° when 10 mA of current is passed through it. If the horizontal component of the earth's magnetic field is `B_H = 3.6 xx 10^-5 "T"` and radius of the coil is 10 cm, find the number of turns in the coil.
The magnetic susceptibility of platinum is 0.0001. It's relative permeability is:
Two substances A and B have their relative permeability slightly greater and slightly less than 1 respectively. What do you conclude about A and B as far as their magnetic materials are concerned?
Identify the following magnetic materials :
Which of the following statements is correct for diamagnetic materials?
Choose the correct option:
A magnetising field of 360 Am−1 produces a magnetic flux density (B) = 0.6T in a ferromagnetic material. What is its permeability in Tm A−1?
The susceptibility of a paramagnetic material is χ at 27° C. At what temperature its susceptibility be χ/3?
Two identical bar magnets each of magnetic moment M, separated by some distance are kept perpendicular to each other. The magnetic induction at a point at the same distance d from the centre of magnets, is (µ0 = permeability of free space)
A domain in a ferromagnetic substance is in the form of a cube of side 1 µm. If it contains 8 × 1010 atoms and each atomic dipole has a dipole moment of 9 × 10-24 Am2 then the magnetisation of the domain is ______.
The susceptibility of a magnetic material is positive and small. The material is ______.
The magnetic susceptibility of a paramagnetic material at - 73 °C is 0.0075. Its value at -173 °C will be ______.
All atoms of a magnetic substance have a resultant magnetic moment even in absence of external magnetic field. The substance is ______.
Magnetization of the sample is ______.
Magnetic material can be easily magnetized if magnetic susceptibility is ______.
Above the curie temperature the susceptibility of ferromagnetic substance varies ____________.
A domain in a ferromagnetic substance is in the form of a cube of side length 1 µm. If it contains 6 x 1010 atoms and each atomic dipole has a dipole moment of 7 x 10-24 Am2, then magnetization of the domain is ____________.
The earth’s field departs from its dipole shape substantially at large distances (greater than about 30,000 km). What agencies may be responsible for this distortion?
A short bar magnet has a magnetic moment of 0.48 J T−1. Give the direction and magnitude of the magnetic field produced by the magnet at a distance of 10 cm from the centre of the magnet on
- the axis,
- the equatorial lines (normal bisector) of the magnet.
Which graph shows the variation of magnetic susceptibility (`chi`) with magnetizing field (H) for a paramagnetic substance?
If a toroid uses bismuth for its core, will the field in the core be (slightly) greater or (slightly) less than when the core is empty?
Explain qualitatively on the basis of domain picture the irreversibility in the magnetisation curve of a ferromagnet.
Assertion: The ferromagnetic substance do not obey Curie’s law.
Reason: At Curie point a ferromagnetic substance start behaving as a paramagnetic substance.
Metals getting magnetised by orientation of atomic magnetic moments in external magnetic field are called ______.
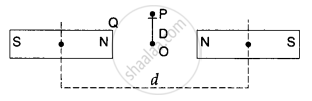
Two identical bar magnets are fixed with their centres at a distance d apart. A stationary charge Q is placed at P in between the gap of the two magnets at a distance D from the centre O as shown in the figure. The force on the charge Q is ______.
The magnetic susceptibility for diamagnetic materials is ______.
When a ferromagnetic material is created above its curie temperature
A hydrogen atom is paramagnetic. A hydrogen molecule is
If a charged particle at rest experience no electromagnetic force
According to the Atomic theory, on heating a magnet, the thermal energy of the elementary magnet ______
A permanent magnet in the shape of a thin cylinder of length 10 cm has M = 106 A/m. Calculate the magnetisation current IM.
Explain quantitatively the order of magnitude difference between the diamagnetic susceptibility of N2 (~5 × 10–9) (at STP) and Cu (~10–5).
Magnetic susceptibility for a paramagnetic and diamagnetic materials is respectively ______.
An ammeter of resistance R gives a full-scale deflection when a current of 2 A passes through it. If it is measured with a maximum current of 10 A, the required shunt is ______.
Which of the following has a permeability less than that of free space?
Explain the Domain theory in brief.
Explain the meaning of the following statement:
Curie temperature for soft iron is 770°C.
