Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A meter gauge train is heading north with speed 54 km/hr in earth's magnetic field 3 x 10-4T. The e.m.f. induced across the axle joining the wheels is ..........
(a) 0.45 mV
(b) 4.5 mV
(c) 45 mV
(d) 450 m V
Solution
(b) 4.5 mV
e = vlb
`= 54 xx 5/18 xx 1 xx 3 xx 10^(-4)`
`= 45 xx 10^(-4) = 4.5 mV`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Which of the following substances is ductile?
Give any ‘two’ points of differences between diamagnetic and ferromagnetic substances.
An iron rod of the area of cross-section 0.1m2 is subjected to a magnetizing field of 1000 A/m. Calculate the magnetic permeability of the iron rod. [Magnetic susceptibility of iron = 59.9, magnetic permeability of vacuum = 4π x 10-7 S. I. unit]
The magnetic susceptibility of annealed iron at saturation is 4224. Find the permeability of
annealed iron at saturation. (μ0 = 4Π × 10−7 SI unit)
The susceptibility of a magnetic material is 0·9853. Identify the type of magnetic material. Draw the modification of the field pattern on keeping a piece of this material in a uniform magnetic field.
Explain Curie’s law for a paramagnetic substance.
A tangent galvanometer shows a deflection of 45° when 10 mA of current is passed through it. If the horizontal component of the earth's magnetic field is `B_H = 3.6 xx 10^-5 "T"` and radius of the coil is 10 cm, find the number of turns in the coil.
Identify the following magnetic materials :
Answer in brief.
Discuss the Curie law for paramagnetic material.
A paramagnetic gas has 2.0 × 1026 atoms/m with atomic magnetic dipole moment of 1.5 × 10−23 A m2 each. The gas is at 27°C.
- Find the maximum magnetization intensity of this sample.
- If the gas in this problem is kept in a uniform magnetic field of 3 T, is it possible to achieve saturation magnetization? Why?
Two identical bar magnets each of magnetic moment M, separated by some distance are kept perpendicular to each other. The magnetic induction at a point at the same distance d from the centre of magnets, is (µ0 = permeability of free space)
For a paramagnetic substance, the magnetic susceptibility is ______.
The susceptibility of a magnetic material is positive and small. The material is ______.
The magnetic susceptibility of a paramagnetic material at - 73 °C is 0.0075. Its value at -173 °C will be ______.
Magnetization of the sample is ______.
There are three needles 'N1', 'N2' and 'N3' made of a ferromagnetic, a paramagnetic and a diamagnetic substance respectively. When a magnet is brought close to them, then it will ____________.
The materials having negative magnetic susceptibility are ____________.
The product of magnetic susceptibility (`chi`) and absolute temperature (T) is constant for a ____________.
Above the curie temperature the susceptibility of ferromagnetic substance varies ____________.
A domain in a ferromagnetic substance is in the form of a cube of side length 1 µm. If it contains 6 x 1010 atoms and each atomic dipole has a dipole moment of 7 x 10-24 Am2, then magnetization of the domain is ____________.
A short bar magnet has a magnetic moment of 0.48 J T−1. Give the direction and magnitude of the magnetic field produced by the magnet at a distance of 10 cm from the centre of the magnet on
- the axis,
- the equatorial lines (normal bisector) of the magnet.
Why does a paramagnetic sample display greater magnetisation (for the same magnetising field) when cooled?
If a toroid uses bismuth for its core, will the field in the core be (slightly) greater or (slightly) less than when the core is empty?
Is the permeability of a ferromagnetic material independent of the magnetic field? If not, is it more for lower or higher fields?
Magnetic field lines are always nearly normal to the surface of a ferromagnet at every point. (This fact is analogous to the static electric field lines being normal to the surface of a conductor at every point.) Why?
Explain qualitatively on the basis of domain picture the irreversibility in the magnetisation curve of a ferromagnet.
A Rowland ring of mean radius 15 cm has 3500 turns of wire wound on a ferromagnetic core of relative permeability 800. What is the magnetic field B in the core for a magnetising current of 1.2 A?
The given figure represents a material which is ______.
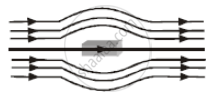
The coercivity of a small magnet where the ferromagnet gets demagnetized is 3 × 103 Am–1. The current required to be passed in a solenoid of length 10 cm and number of turns 100, so that the magnet gets demagnetized when inside the solenoid, is ______.
Metals getting magnetised by orientation of atomic magnetic moments in external magnetic field are called ______.
Which of the following property shows the property of ferromagnetic substances?
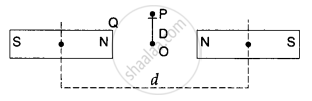
Two identical bar magnets are fixed with their centres at a distance d apart. A stationary charge Q is placed at P in between the gap of the two magnets at a distance D from the centre O as shown in the figure. The force on the charge Q is ______.
The magnetic susceptibility for diamagnetic materials is ______.
When a ferromagnetic material is created above its curie temperature
For a diamagnetic material
If a charged particle at rest experience no electromagnetic force
The universal property of all substances is ______.
A long solenoid has 1000 turns per metre and carries a current of 1 A. It has a soft iron core of µr = 1000. The core is heated beyond the Curie temperature, Tc.
- The H field in the solenoid is (nearly) unchanged but the B field decreases drastically.
- The H and B fields in the solenoid are nearly unchanged.
- The magnetisation in the core reverses direction.
- The magnetisation in the core diminishes by a factor of about 108.
From molecular view point, discuss the temperature dependence of susceptibility for diamagnetism, paramagnetism and ferromagnetism.
A uniform magnetic field gets modified as shown in figure when two specimens A and B are placed in it.
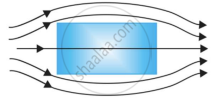 |
 |
| (a) | (b) |
- Identify the specimen A and B.
- How is the magnetic susceptibility of specimen A different from that of specimen B?
- Assertion (A): Diamagnetic substances exhibit magnetism.
- Reason (R): Diamagnetic materials do not have a permanent magnetic dipole moment.
The relative magnetic permeability of a substance X is slightly less than unity and that of substance Y is slightly more than unity, then ______.
Explain ferromagnetism on the basis of the domain theory.
State the dimensions of magnetization.
Explain the Domain theory in brief.
Magnetic susceptibility of a diamagnetic substance ______.
