Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Which of the following substances is ductile?
Options
Glass
High carbon steel
Steel
Copper
Solution
Copper
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Distinguish between ‘paramagnetic’ and ‘ferromagnetic’ substances.
Give any ‘two’ points of differences between diamagnetic and ferromagnetic substances.
The susceptibility of magnesium at 200 K is 1.8 x 10-5. At what temperature will the susceptibility decrease by 6 x 10-6?
In what way is the behaviour of a diamagnetic material different from that of a paramagnetic, when kept in an external magnetic field?
Distinguish between diamagnetic and paramagnetic substances
A meter gauge train is heading north with speed 54 km/hr in earth's magnetic field 3 x 10-4T. The e.m.f. induced across the axle joining the wheels is ..........
(a) 0.45 mV
(b) 4.5 mV
(c) 45 mV
(d) 450 m V
Explain Curie’s law for a paramagnetic substance.
Which of the following substances are diamagnetic?
Bi, Al, Na, Cu, Ca and Ni
The susceptibility of a magnetic material is − 2.6 × 10−5. Identify the type of magnetic material and state its two properties.
Draw magnetic field line when a (i) diamagnetic, (ii) paramagnetic substance is placed in an external magnetic field. Which magnetic property distinguishes this behaviour of the field line due to the substances?
Choose the correct option:
A magnetising field of 360 Am−1 produces a magnetic flux density (B) = 0.6T in a ferromagnetic material. What is its permeability in Tm A−1?
The susceptibility of a paramagnetic material is χ at 27° C. At what temperature its susceptibility be χ/3?
All atoms of a magnetic substance have a resultant magnetic moment even in absence of external magnetic field. The substance is ______.
Magnetization of the sample is ______.
Relative permittivity and permeability of a material are `epsilon_"r"` and `µ_"r"` respectively. Which of the following values of these quantities are allowed for a diamagnetic material?
The materials having negative magnetic susceptibility are ____________.
The magnetic property of magnetic substance is associated with ____________.
Above the curie temperature the susceptibility of ferromagnetic substance varies ____________.
A small quantity of paramagnetic liquid is taken in a watch - glass and kept on two dissimilar magnetic poles. The liquid ____________.
Magnetic field lines are always nearly normal to the surface of a ferromagnet at every point. (This fact is analogous to the static electric field lines being normal to the surface of a conductor at every point.) Why?
Explain qualitatively on the basis of domain picture the irreversibility in the magnetisation curve of a ferromagnet.
What kind of ferromagnetic material is used for coating magnetic tapes in a cassette player, or for building ‘memory stores’ in a modern computer?
A certain region of space is to be shielded from magnetic fields. Suggest a method.
A Rowland ring of mean radius 15 cm has 3500 turns of wire wound on a ferromagnetic core of relative permeability 800. What is the magnetic field B in the core for a magnetising current of 1.2 A?
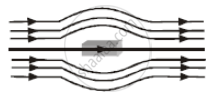
The given figure represents a material which is ______.
The coercivity of a small magnet where the ferromagnet gets demagnetized is 3 × 103 Am–1. The current required to be passed in a solenoid of length 10 cm and number of turns 100, so that the magnet gets demagnetized when inside the solenoid, is ______.
The magnetic susceptibility is negative for ______.
When a ferromagnetic material is created above its curie temperature
If a charged particle at rest experience no electromagnetic force
A paramagnetic sample shows a net magnetisation of 8 Am–1 when placed in an external magnetic field of 0.6 T at a temperature of 4 K. When the same sample is placed in an external magnetic field of 0.2 T at a temperature of 16 K, the magnetisation will be ______.
Explain quantitatively the order of magnitude difference between the diamagnetic susceptibility of N2 (~5 × 10–9) (at STP) and Cu (~10–5).
From molecular view point, discuss the temperature dependence of susceptibility for diamagnetism, paramagnetism and ferromagnetism.
An ammeter of resistance R gives a full-scale deflection when a current of 2 A passes through it. If it is measured with a maximum current of 10 A, the required shunt is ______.
- Assertion (A): Diamagnetic substances exhibit magnetism.
- Reason (R): Diamagnetic materials do not have a permanent magnetic dipole moment.
What is magnetic hysterisis?
Explain the origin of paramagnetism on the basis of atomic structure.
State the dimensions of magnetization.
