Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Which of the following substances is ductile?
पर्याय
Glass
High carbon steel
Steel
Copper
उत्तर
Copper
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The susceptibility of magnesium at 200 K is 1.8 x 10-5. At what temperature will the susceptibility decrease by 6 x 10-6?
In what way is the behaviour of a diamagnetic material different from that of a paramagnetic, when kept in an external magnetic field?
Show diagrammatically the behaviour of magnetic field lines in the presence of (i) paramagnetic and (ii) diamagnetic substances. How does one explain this distinguishing feature?
A meter gauge train is heading north with speed 54 km/hr in earth's magnetic field 3 x 10-4T. The e.m.f. induced across the axle joining the wheels is ..........
(a) 0.45 mV
(b) 4.5 mV
(c) 45 mV
(d) 450 m V
Which of the following substances are diamagnetic?
Bi, Al, Na, Cu, Ca and Ni
Which of the following substances are para-magnetic?
Bi, Al, Cu, Ca, Pb, Ni
The susceptibility of a magnetic material is − 2.6 × 10−5. Identify the type of magnetic material and state its two properties.
The relative magnetic permeability of a magnetic material is 800. Identify the nature of magnetic material and state its two properties.
A tangent galvanometer shows a deflection of 45° when 10 mA of current is passed through it. If the horizontal component of the earth's magnetic field is `B_H = 3.6 xx 10^-5 "T"` and radius of the coil is 10 cm, find the number of turns in the coil.
Answer the following question.
Write three points of differences between para-, dia- and ferromagnetic materials, giving one example for each.
Identify the following magnetic materials :
Choose the correct option:
A rectangular magnet suspended freely has a period of oscillation equal to T. Now it is broken into two equal halves (each having half of the original length) and one piece is made to oscillate freely. Its period of oscillation is T′, the ratio of T′/T is ______.
Choose the correct option:
A magnetising field of 360 Am−1 produces a magnetic flux density (B) = 0.6T in a ferromagnetic material. What is its permeability in Tm A−1?
What happens to a ferromagnetic material when its temperature increases above curie temperature?
A paramagnetic gas has 2.0 × 1026 atoms/m with atomic magnetic dipole moment of 1.5 × 10−23 A m2 each. The gas is at 27°C.
- Find the maximum magnetization intensity of this sample.
- If the gas in this problem is kept in a uniform magnetic field of 3 T, is it possible to achieve saturation magnetization? Why?
Two identical bar magnets each of magnetic moment M, separated by some distance are kept perpendicular to each other. The magnetic induction at a point at the same distance d from the centre of magnets, is (µ0 = permeability of free space)
For a paramagnetic substance, the magnetic susceptibility is ______.
The magnetic susceptibility of a paramagnetic material at - 73 °C is 0.0075. Its value at -173 °C will be ______.
All atoms of a magnetic substance have a resultant magnetic moment even in absence of external magnetic field. The substance is ______.
If a magnetic field is applied to a liquid in one arm of a narrow U-tube, the liquid level in that arm is lowered. The liquid in U-tube arm is ______.
There are three needles 'N1', 'N2' and 'N3' made of a ferromagnetic, a paramagnetic and a diamagnetic substance respectively. When a magnet is brought close to them, then it will ____________.
The materials having negative magnetic susceptibility are ____________.
The magnetic property of magnetic substance is associated with ____________.
The product of magnetic susceptibility (`chi`) and absolute temperature (T) is constant for a ____________.
A small quantity of paramagnetic liquid is taken in a watch - glass and kept on two dissimilar magnetic poles. The liquid ____________.
A domain in a ferromagnetic substance is in the form of a cube of side length 1 µm. If it contains 6 x 1010 atoms and each atomic dipole has a dipole moment of 7 x 10-24 Am2, then magnetization of the domain is ____________.
The earth’s field departs from its dipole shape substantially at large distances (greater than about 30,000 km). What agencies may be responsible for this distortion?
A short bar magnet has a magnetic moment of 0.48 J T−1. Give the direction and magnitude of the magnetic field produced by the magnet at a distance of 10 cm from the centre of the magnet on
- the axis,
- the equatorial lines (normal bisector) of the magnet.
Which graph shows the variation of magnetic susceptibility (`chi`) with magnetizing field (H) for a paramagnetic substance?
Why does a paramagnetic sample display greater magnetisation (for the same magnetising field) when cooled?
Why is diamagnetism, in contrast, almost independent of temperature?
If a toroid uses bismuth for its core, will the field in the core be (slightly) greater or (slightly) less than when the core is empty?
Magnetic field lines are always nearly normal to the surface of a ferromagnet at every point. (This fact is analogous to the static electric field lines being normal to the surface of a conductor at every point.) Why?
Explain qualitatively on the basis of domain picture the irreversibility in the magnetisation curve of a ferromagnet.
The given figure represents a material which is ______.
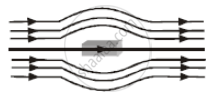
Metals getting magnetised by orientation of atomic magnetic moments in external magnetic field are called ______.
Which of the following property shows the property of ferromagnetic substances?
The magnetic susceptibility for diamagnetic materials is ______.
For a diamagnetic material
The universal property of all substances is ______.
According to the Atomic theory, on heating a magnet, the thermal energy of the elementary magnet ______
A paramagnetic sample shows a net magnetisation of 8 Am–1 when placed in an external magnetic field of 0.6 T at a temperature of 4 K. When the same sample is placed in an external magnetic field of 0.2 T at a temperature of 16 K, the magnetisation will be ______.
Explain quantitatively the order of magnitude difference between the diamagnetic susceptibility of N2 (~5 × 10–9) (at STP) and Cu (~10–5).
Which of the following cannot modify an external magnetic field as shown in the figure?

Explain the Domain theory in brief.
Explain the meaning of the following statement:
Curie temperature for soft iron is 770°C.
