Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
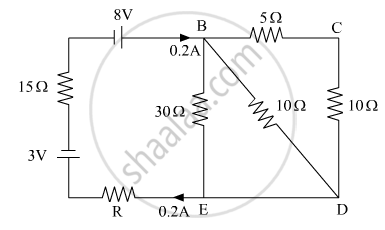
Calculate the value of the resistance R in the circuit shown in the figure so that the current in the circuit is 0.2 A. What would b the potential difference between points B and E?
उत्तर
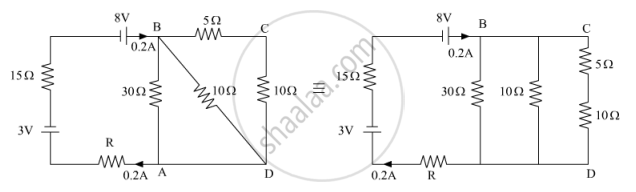
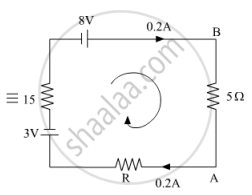
Apply Kirchhoff’s Law:-
5(0.2) + R (0.2) + 15(0.2) = 8 − 3
⇒ R = 5Ω
VBE = 5(0.2) = 1V
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Kirchhoff's voltage law and current law are respectively in accordance with the conservation of .................................. .
- charge and momentum
- charge and energy
- energy and charge
- energy and momentum
Use Kirchhoff's rules to obtain conditions for the balance condition in a Wheatstone bridge.
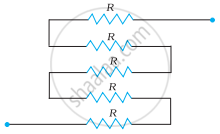
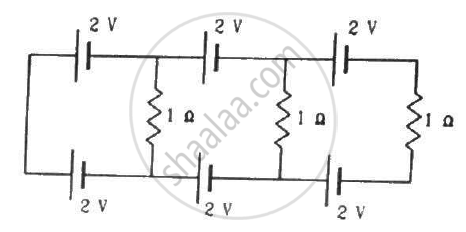
Determine the equivalent resistance of networks shown in Fig.
In the given circuit, assuming point A to be at zero potential, use Kirchhoff’s rules to determine the potential at point B.

Find the circuit in the three resistors shown in the figure.
Lightning is a very good example of a natural current. In typical lightning, there is 109 J energy transfer across the potential difference of 5 × 107 V during a time interval of 0.2 s. Using this information, estimate the following quantities:
- the total amount of charge transferred between cloud and ground
- the current in the lightning bolt
- the power delivered in 0.2 s.

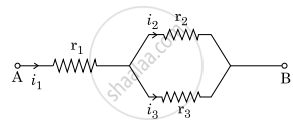
Three resistors having resistances r1, r2 and r3 are connected as shown in the given circuit. The ratio `"i"_3/"i"_1` of currents in terms of resistances used in the circuit is :
Power P is to be delivered to a device via transmission cables having resistance RC. If V is the voltage across R and I the current through it, find the power wasted and how can it be reduced.
Derive the equation of the balanced state in a Wheatstone bridge using Kirchhoff’s laws.
The figure below shows two batteries, E1 and E2, having emfs of 18V and 10V and internal resistances of 1 Ω and 2 Ω, respectively. W1, W2 and W3 are uniform metallic wires AC, FD and BE having resistances of 8 Ω, 6 Ω and 10 Ω respectively. B and E are midpoints of the wires W1 and W2. Using Kirchhoff's laws of electrical circuits, calculate the current flowing in the wire W3:

