Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
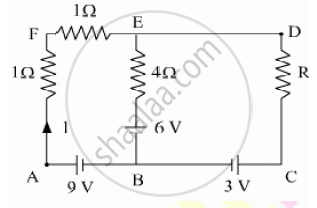
Find the circuit in the three resistors shown in the figure.
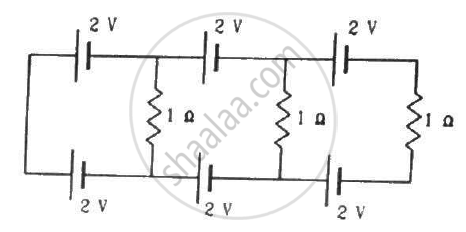
उत्तर
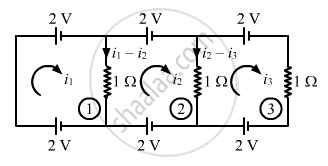
Applying KVL in loop 1, we get:-
\[2 + \left( i_1 - i_2 \right) \times 1 - 2 = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow i_1 = i_2\]
Applying KVL in loop 2, we get:-
\[2 + \left( i_2 - i_3 \right) \times 1 - 2 - \left( i_1 - i_2 \right) \times 1 = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow i_2 - i_3 - i_1 + i_2 = 0\]
\[ i_1 = i_2 \]
\[ \Rightarrow i_2 - i_3 - i_2 + i_2 = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow i_2 = i_3\]
Applying KVL in loop 3, we get:-
\[2 + i_3 - 2 - \left( i_2 - i_3 \right) = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow i_3 = 0\]
\[ i_1 = i_2 = i_3 \]
\[ \therefore i_1 = i_2 = i_3 = 0\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Kirchhoff's junction law is equivalent to .............................
(a) conservation of energy.
(b) conservation of charge
(c) conservation of electric potential
(d) conservation of electric flux
State the two Kirchhoff’s rules used in electric networks. How are there rules justified?
Use Kirchhoff's rules to obtain conditions for the balance condition in a Wheatstone bridge.
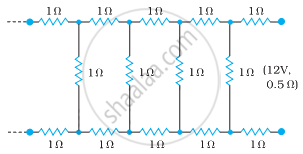
Determine the current drawn from a 12 V supply with internal resistance 0.5 Ω by the infinite network shown in the figure. Each resistor has 1 Ω resistance.
Given the resistances of 1 Ω, 2 Ω, 3 Ω, how will be combine them to get an equivalent resistance of 6 Ω?
State Kirchhoff's rules for an electric network. Using Kirchhoff's rules, obtain the balance condition in terms of the resistances of four arms of Wheatstone bridge.
Using Kirchhoff’s rules determine the value of unknown resistance R in the circuit so that no current flows through 4 Ω resistance. Also find the potential difference between A and D.
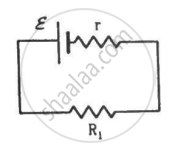
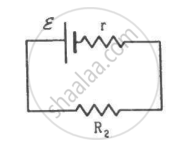
Two unequal resistances, R1 and R2, are connected across two identical batteries of emf ε and internal resistance r (see the figure). Can the thermal energies developed in R1 and R2 be equal in a given time? If yes, what will be the condition?
On which conservation principle is Kirchoff's Second Law of electrical networks based?
State Kirchhoff’s current rule.
State Kirchhoff ’s voltage rule.
State and explain Kirchhoff’s rules.
While measuring the length of the rod by vernier callipers, the reading on the main scale is 6.4 cm and the eight divisions on vernier is in line with marking on the main scale division. If the least count of callipers is 0.01 and zero error - 0.04 cm, the length of the rod is ______.
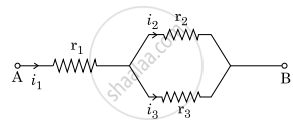
Three resistors having resistances r1, r2 and r3 are connected as shown in the given circuit. The ratio `"i"_3/"i"_1` of currents in terms of resistances used in the circuit is :
In a meter bridge the point D is a neutral point (Figure).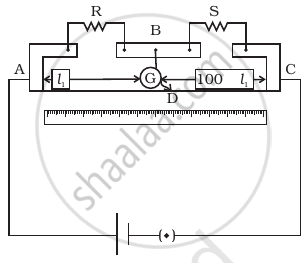
- The meter bridge can have no other neutral point for this set of resistances.
- When the jockey contacts a point on meter wire left of D, current flows to B from the wire.
- When the jockey contacts a point on the meter wire to the right of D, current flows from B to the wire through galvanometer.
- When R is increased, the neutral point shifts to left.
What are the advantages of the null-point method in a Wheatstone bridge? What additional measurements would be required to calculate `R_(unknown)` by any other method?
Why are alloys used for making standard resistance coils?
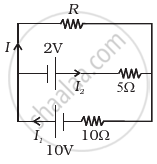
Two cells of voltage 10V and 2V and internal resistances 10Ω and 5Ω respectively, are connected in parallel with the positive end of 10V battery connected to negative pole of 2V battery (Figure). Find the effective voltage and effective resistance of the combination.
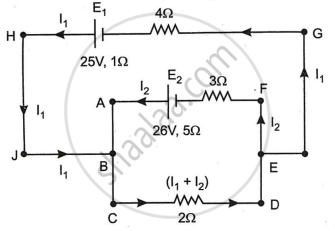
In the circuit shown in Figure below, E1 and E2 are batteries having emfs of 25V and 26V. They have an internal resistance of 1 Ω and 5 Ω respectively. Applying Kirchhoff’s laws of electrical networks, calculate the currents I1 and I2.