Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Define electric flux.
Define electric flux. Is it a scalar or a vector quantity?
उत्तर १
Electric flux is the total number of lines of force passing through the unit area of a surface held perpendicularly.
Electric flux ΔΦ through an area element ΔS is given by
ΔΦ = E.ΔS = EΔScosθ
θ is the angle between E and ΔS.
उत्तर २
Electric flux is defined as the number of electric field lines crossing the per unit area. It is given as
`triangle phi = vecE.vec(triangleS) cos theta`
where `vecE` is Electric field and `vec(triangleS)`is area vector. The angle θ here is the angle between `vecE` and `vec(triangle S)`.
Since Electric flux is the dot product of two vectors, Hence it is a Scalar quantity.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Given a uniform electric filed \[\vec{E} = 4 \times {10}^3 \ \hat{i} N/C\]. Find the flux of this field through a square of 5 cm on a side whose plane is parallel to the Y-Z plane. What would be the flux through the same square if the plane makes a 30° angle with the x-axis?
Two charges of magnitudes −3Q and + 2Q are located at points (a, 0) and (4a, 0) respectively. What is the electric flux due to these charges through a sphere of radius ‘5a’ with its centre at the origin?
A thin straight infinitely long conducting wire having charge density λ is enclosed by a cylindrical surface of radius r and length l, its axis coinciding with the length of the wire. Find the expression for the electric flux through the surface of the cylinder.
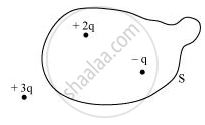
Figure shows three point charges +2q, −q and + 3q. Two charges + 2q and −q are enclosed within a surface ‘S’. What is the electric flux due to this configuration through the surface ‘S’?
A small plane area is rotated in an electric field. In which orientation of the area, is the flux of the electric field through the area maximum? In which orientation is it zero?
If the flux of the electric field through a closed surface is zero,
(a) the electric field must be zero everywhere on the surface
(b) the electric field may be zero everywhere on the surface
(c) the charge inside the surface must be zero
(d) the charge in the vicinity of the surface must be zero
The electric field intensity due to an infinite cylinder of radius R and having charge q per unit length at a distance rir r(r > R) from its axis is ______.
If the electric flux entering and leaving an enclosed surface respectively is Φ1 and Φ2, the electric charge inside the surface will be
A hollow sphere of radius R has a point charge q at its centre. Electric flux emanating from the sphere is X. How will the electric flux change, if at all, when radius of the sphere is doubled?
