Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
उत्तर
Linear magnification is defined as the ratio of the height of the image to the height of the object. It is taken to be positive for an image to be virtual and erect and negative when image is real and inverted.
Magnification = height of image / height of object.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define the following term in the context of spherical mirrors:- Centre of curvature
A concave mirror always forms a real image.
Define the Focal length of a spherical mirror
What happens when a ray of light falls normally (or perpendiculary) on the surface of a plane mirror?
A coin placed at the bottom of a vessel appears to be raised when water is poured in the vessel.
AB and CD, two spherical mirrors, from parts of a hollow spherical ball with its centre at O as shown in the diagram. If arc AB = `1/2` arc CD, what is the ratio of their focal lengths? State which of the two mirrors will always form virtual image of an object placed in front of it and why.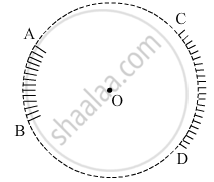
Name the mirrors shown in Figure (a) and (b).
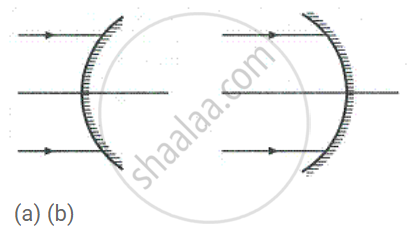
Does the mirror mentioned in part (b) form real image for all locations of the object?
An object 5 cm high forms a virtual image of 1.25 cm high, when placed in front of a convex mirror at a distance of 24 cm. Calculate:
- the position of the image
- the focal length of the convex mirror.
If the real image of a candle flame formed by a lens is three times the size of the flame and the distance between lens and image is 80 cm, at what distance should the candle be placed from the lens?
