Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
उत्तर
Critical angle is the angle of incidence in the denser medium for which the angle of refraction in the rarer medium is 90o.
Total internal reflection: When a ray of light travelling from an optically denser medium to an optically rare medium is incident at an angle greater than the critical angle for the pair of media in contact, the ray is totally reflected back into the denser medium. This phenomenon is referred as total internal reflection.
The two necessary conditions for total internal reflection to take place are:
1. The light ray must proceed from denser to rarer medium.
2. Angle of incidence in denser medium should be greater than the critical angle for the pair of media in contact.
Relation between critical angle and r.i.: The critical angle can thus be calculated by taking the inverse-sine ratio of speed of light in denser medium and the speed of light in rarer.
ic = sin -1 `(("n"gamma)/("n"_i))`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State the relation between the critical angle and the absolute refractive index of a medium.
Angle of deviation is the angle which the ______ ray makes with the direction of ______ray.
Total internal reflection occurs only when a ray of light passes from a ______ medium to a ______ medium.
In the given figure PQ and PR are the two light rays emerging from an object P. The ray PQ is refracted as QS.
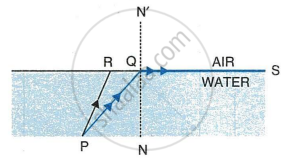
- State the special name given to the angle of incidence ∠PQN of the ray PQ.
- What is the angle of refraction for the refracted ray QS?
- Name the phenomenon that occurs if the angle of incidence ∠PQN is increased.
- The ray PR suffers partial reflection and refraction on the water-air surface. Give reason.
- Draw in the diagram the refracted ray for the incident ray PR and hence show the position of image of the object P by the letter P’ when seen vertically from above.
Name the principle on the basis of which optical fibres work.
The resultant `vec"R"` of `vec"P"` and `vec"Q"` is perpendicular to `vec"P"`. Also `|vec"P"|=|vec"R"|`. The angle between `vec"P"` and `vec"Q"` is ______.
[tan 45° = 1]
What is a mirage? How does it occur?
What are the examples of total internal reflection in nature?
A rectangular block of glass ABCD has a refractive index 1.6. A pin is placed midway on the face AB (Figure). When observed from the face AD, the pin shall ______.
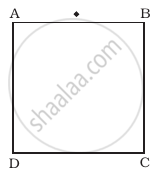
- appear to be near A.
- appear to be near D.
- appear to be at the centre of AD.
- not be seen at all.
