Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Define the following term:
Photolysis of water
उत्तर
Releasing electrons and dividing the water molecule (H2O) into its two components (Hydrogen and Oxygen). Photolysis is the term used to describe this reaction, which is characterised by the fracturing of molecules by light (photo = light, lysis = breaking).
संबंधित प्रश्न
The following diagram demonstrates a physiological process taking place in green plants. The whole set up was placed in bright sunlight for several hours. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow

(i) What aspect of the physiological process is being examined?
(ii) Explain the physiological process mentioned in (i) above.
(iii) Label the parts numbered 1 and 2 in the diagram.
(iv) Write a well-balanced chemical equation for the physiological process explained in (ii) above.
(v) What would happen to the rate of bubbling of the gas if a pinch of sodium bicarbonate is added to the water in the beaker? Explain your answer.
Given below is an experiment setup to demonstrate a particualr tropic movement in germinating seeds. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow :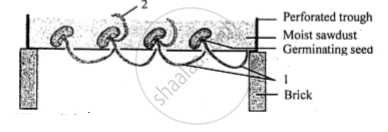
(ii) Name the tropic movement shown by part 1.
The following statement is about photosynthesis in a green plant. Write whether it is True or False.
The raw materials for photosynthesis include water and carbon dioxide.
Complete the following by filling in the blanks numbered 1 to 10 with the appropriate word/term:
Photosynthesis involves light reaction and dark reaction. During light reaction, the chlorophyll present in the (1) ______ gets activated by absorbing light energy. This energy splits (2) ______ molecules to (3) ______ and oxygen and releases two electrons. This process is called (4) ______. The (5) ______ ions are picked up by NADP to form (6) ______. The ADP is converted to (7) ______. This process is called (8) ______. During the dark phase, the compound produced at the end of the light reaction reacts with carbon dioxide to form (9) ______. This product is converted to starch. The process is called (10) ______.
Choose the correct answer:
Photosynthesis is more active in ___________
A candidate studied the importance of certain factors in photosynthesis. He took a potted plant and kept in the dark for over 24 hours. In the early hours of the next morning, he covered one of the leaves with black paper in the centre only. Then he placed the plant in sunlight for a few hours and tested the leaf which was covered with black paper for starch.
Is there any control in this experiment? If so, state it.
Photosynthesis in green plants is directly and indirectly dependent on so many plant structures.
Explain briefly the role of the following structures in this process is Stomata.
Give some adaptations in green leaf photosynthesis.
Oxygen given out during photosynthesis comes from water. Explain this statement.
Draw a neat and well-labeled diagram of the apparatus you would set up to show that oxygen is given out during photosynthesis.
Explain the Term Calvin Cycle.
Give technical term:
What is the percentage of CO2 in the air?
Answer the following question.
Explain why photosynthesis is considered the most important process in the biosphere.
Why should the light-dependent reaction occur before the light-independent reaction?
Where do the light-dependent reaction and the Calvin cycle occur in the chloroplast?
Oxygen is used for the synthesis of protein and fertilizers.
The raw materials for photosynthesis are ______ and ______.
Study the pictures below and then complete the table by putting a plus (+) if the shoot or root grows towards the stimulus and a minus (-) if it grows away from it.

| Stimulus | Light | Gravity |
| Shoot | + | - |
| Root | ? | + |
Mention four factors required for photosynthesis?
