Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Define the term principal foci as applied to a concave lens. Illustrate your answer with the aid of proper diagrams. Show the focal length of the lens in the diagram.
उत्तर
A concave lens has two principal foci:
(i) first focus and
(ii) second focus.
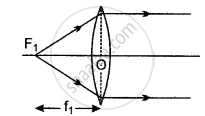
(i) First focus: First focus of a concave lens is point F1 on the principal axis of the lens such that the rays of light appearing to meet at it, after refraction from the lens becomes parallel to the principal axis. This is shown in the figure. The distance of first point F1 from the optical centre O of the lens (i.e., OF1) is the first focal length f1.
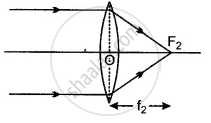
(ii) Second focus: Second focus of a concave lens is the point F2 on the principal axis of the lens such that the rays of light incident parallel to the principal axis of the lens after refraction from the lens appears to be coming from it. This is shown in the figure. The distance of the second focal point F2 from the optical centre O of the lens (i.e., OF2) is called the second focal length f2.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Where must the object be placed for the image formed by a converging lens to be:
real, inverted and larger than the object?
State whether concave lens has a real focus or a virtual focus.
If an object is placed 21 cm from a converging lens, the image formed is slightly smaller than the object. If the object is placed 19 cm from the lens, the image formed is slightly larger than object. The approximate focal length of the lens is ______.
Show by drawing a ray-diagram that the image of an object formed by a concave lens is virtual, erect and diminished.
With the help of a diagram, explain why the image of an object viewed through a concave lens appears smaller and closer than the object.
When sunlight is concentrated on a piece of paper by a spherical mirror or lens, then a hole can be burnt in it. For doing this, the paper must be placed at he focus of:
(a) either a convex mirror or convex lens
(b) either a concave mirror or concave lens
(c) either a concave mirror or convex lens
(d) either a convex mirror or concave lens
An object is placed on the axis of a lens. An image is formed by refraction in the lens. For all positions of the object on the axis of the lens, the positions of the image are always always between the lens and the object Draw a ray diagram to show it.
At what distance from a concave lens of focal length 20 cm a 6 cm tall object be placed so as to obtain its image at 15 cm from the lens? Also calculate the size of the image formed.
Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer for the above situation and label it.
Distinguish between concave and convex lens.
An object is placed in front of a lens between its optical centre and focus. The formed image is virtual, erect, and diminished. Name the lens used.
