Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Define the term principal foci as applied to a concave lens. Illustrate your answer with the aid of proper diagrams. Show the focal length of the lens in the diagram.
Solution
A concave lens has two principal foci:
(i) first focus and
(ii) second focus.
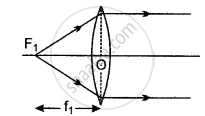
(i) First focus: First focus of a concave lens is point F1 on the principal axis of the lens such that the rays of light appearing to meet at it, after refraction from the lens becomes parallel to the principal axis. This is shown in the figure. The distance of first point F1 from the optical centre O of the lens (i.e., OF1) is the first focal length f1.
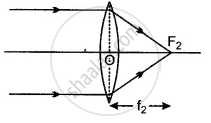
(ii) Second focus: Second focus of a concave lens is the point F2 on the principal axis of the lens such that the rays of light incident parallel to the principal axis of the lens after refraction from the lens appears to be coming from it. This is shown in the figure. The distance of the second focal point F2 from the optical centre O of the lens (i.e., OF2) is called the second focal length f2.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A converging lens of focal length 5 cm is placed at a distance of 20 cm from a screen. How far from the lens should an object be placed so as to form its real image on the screen?
If the image formed by a lens is always diminished and erect, what is the nature of the lens?
Take down this figure into your answer book and complete the path of the ray.
Which type of lens is :
a converging lens, and which is
Construct ray diagrams to illustrate the formation of a virtual image using a converging lens,
State whether the following statement is true or false:
Short-sightedness can be cured by using a concave lens.
Where will the image be formed if an object is kept in front of a concave lens at a distance equal to its focal length? Draw a ray diagram to illustrate your answer.
A concave lens, if kept at a proper distance from an object, can form its real image.
A virtual diminished image is formed when an object is placed between the optical centre and the principal focus of a lens.
(i) Name the type of lens which forms the above image.
(ii) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image with the above stated characteristics.
Convex magnifying glass is called divergent magnifying glass and concave magnifying glass is called converging magnifying glass.
