Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Construct ray diagrams to illustrate the formation of a virtual image using a converging lens,
Solution
When an object is placed between the optic centre and the focus of a converging lens, the image formed is virtual, erect and magnified as shown in the figure.

APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
A convex lens .................. rays of light, whereas a concave lens .................. rays of light.
Show by drawing a ray-diagram that the image of an object formed by a concave lens is virtual, erect and diminished.
When an object is kept at any distance in front of a concave lens, the image formed is always:
(a) virtual, erect and magnified
(b) virtual, inverted and diminished.
(c) virtual, erect and diminished
(d) virtual, erect and same size as object
Calculate the image distance for an object of height 12 mm at a distance of 0.20 m from a concave lens of focal length 0.30 m, and state the nature and size of the image.
If the image formed by a lens is diminished in size and erect, for all positions of the object, what type of lens is it?
Distinguish between concave and convex lens.
A concave lens has a focal length 30 cm. Find the position and magnification (m) of the image for an object placed in front of it at distance 30 cm. State whether the image is real or virtual?
In figure give below of thin concave lens, F1 and F2 are its foci, complete the path of the given ray of light after it emerges out of the lens.
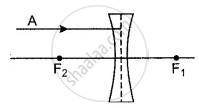
Draw images in case of a concave lens when the object is at any point on the principal axis between the lens and infinity.
Distinguish between Concave lens and Convex Lens.
