Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Construct ray diagrams to illustrate the formation of a virtual image using a converging lens,
उत्तर
When an object is placed between the optic centre and the focus of a converging lens, the image formed is virtual, erect and magnified as shown in the figure.

APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
How would you alter the above diagram to show how a converging lens can produce a beam of parallel rays of light.
What type of image is always made by a concave lens?
Show by drawing a ray-diagram that the image of an object formed by a concave lens is virtual, erect and diminished.
Give the position, size and nature of image of formed by a concave lens when the object is placed:
anywhere between optical centre and infinity.
How would a pencil look like if you saw it through
a concave lens Is the image real or virtual?
Calculate the image distance for an object of height 12 mm at a distance of 0.20 m from a concave lens of focal length 0.30 m, and state the nature and size of the image.
Only one of the following applies to a concave lens. This is:
(a) focal length is positive
(b) image distance can be positive or negative
(c) height of image can be positive or negative
(d) image distance is always negative
How will you differentiate between a convex and a concave lens by looking at
- a distant object,
- a printed page?
The diagrams showing the correct path of the ray after passing through the lens are:
 |
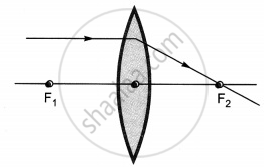 |
| I | II |
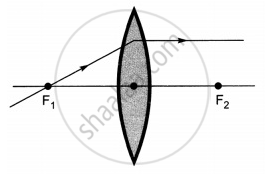 |
 |
| III | IV |
Give two characteristics of the image formed by a concave lens.
