Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
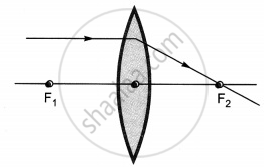
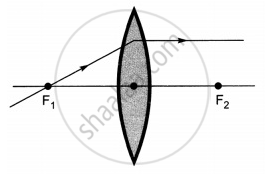
The diagrams showing the correct path of the ray after passing through the lens are:
 |
 |
| I | II |
 |
 |
| III | IV |
पर्याय
II and III only
I and II only
I, II and III
I, II and IV
उत्तर
I, II and III
Explanation:
Ray diagrams (I), (II) and (III) are correct.
The light rays passing through the optical center of lens remain undeflected.
The light rays parallel to the principal axis passes through the second focus of the lens.
The light rays passing through the first focus become parallel to the principal axis after passing through the lens.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a diagram to show how a converging lens focusses parallel rays of light?
Which type of lenses are:
thinner in the middle than at the edges?
Give the position, size and nature of image of formed by a concave lens when the object is placed:
anywhere between optical centre and infinity.
With the help of a diagram, explain why the image of an object viewed through a concave lens appears smaller and closer than the object.
Name one of the common defects of vision and the type of lens used to remove it.
Out of the two lenses, one concave and the other convex, state which one will show the divergent action on a light beam. Draw diagrams to illustrate your answer.
A concave lens forms the image of an object which is ______.
An object is placed in front of a lens between its optical centre and focus. The formed image is virtual, erect, and diminished. Name the lens used.
Copy the following figure and complete it to show the formation of the image of the object AB. Name the lens used in the figure.
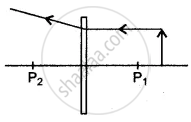
Draw images in case of a concave lens when the object is at infinity.
