Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The diagrams showing the correct path of the ray after passing through the lens are:
 |
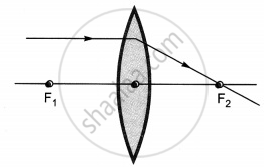 |
| I | II |
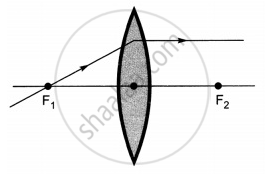 |
 |
| III | IV |
विकल्प
II and III only
I and II only
I, II and III
I, II and IV
उत्तर
I, II and III
Explanation:
Ray diagrams (I), (II) and (III) are correct.
The light rays passing through the optical center of lens remain undeflected.
The light rays parallel to the principal axis passes through the second focus of the lens.
The light rays passing through the first focus become parallel to the principal axis after passing through the lens.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If the numerical value of the power of this lens is 10 D, what is its focal length in the Cartesian system ?
A converging lens is used to produce an image of an object on a screen,object on a screen. What change is needed for the image to be formed nearer to the lens?
(a) increase the focal length of the lens
(b) insert a diverging lens between the lens and the screen
(c) increase the distance of the object from the lens
(d) move the object closer to the lens
If the image formed by a lens is always diminished and erect, what is the nature of the lens?
What type of image is always made by a concave lens?
How would a pencil look like if you saw it through
a concave lens Is the image real or virtual?
A concave lens of focal length 15 cm forms an image 10 cm from the lens. How far is the object placed from the lens? Draw the ray diagram.
An object 60 cm from a lens gives a virtual image at a distance of 20 cm in front of the lens. What is the focal length of the lens? Is the lens converging or diverging? Give reasons for your answer.
A concave lens has focal length 15 cm. At what distance should the object from the lens be placed so that it forms an image at 10 cm from the lens? Also find the magnification produced by the lens.
State three characteristics of the image of an extended source, formed by a concave lens.
Do we expect any change in the position, nature, and size of the image
(i) formed by a concave lens,
(ii) with a change in the position of the object?
