Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
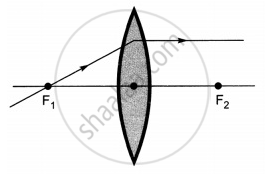
The diagrams showing the correct path of the ray after passing through the lens are:
 |
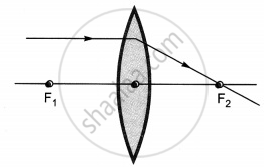 |
| I | II |
 |
 |
| III | IV |
Options
II and III only
I and II only
I, II and III
I, II and IV
Solution
I, II and III
Explanation:
Ray diagrams (I), (II) and (III) are correct.
The light rays passing through the optical center of lens remain undeflected.
The light rays parallel to the principal axis passes through the second focus of the lens.
The light rays passing through the first focus become parallel to the principal axis after passing through the lens.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A converging lens of focal length 5 cm is placed at a distance of 20 cm from a screen. How far from the lens should an object be placed so as to form its real image on the screen?
An object 2 cm tall stands on the principal axis of a converging lens of focal length 8 cm. Find the position, nature and size of the image formed if the object is:
(i) 12 cm from the lens
(ii) 6 cm from the lens
State one practical application each of the use of such a lens with the object in position (i) and (ii).
Copy and complete the diagram below to show what happens to the rays of light when they pass through the concave lens:
When an object is placed 10 cm in front of lens A, the image is real, inverted, magnified and formed at a great distance. When the same object is placed 10 cm in front of lens B, the image formed is real, inverted and same size as the object.
What is the focal length of lens B?
(a) Find the position and size of the virtual image formed when an object 2 cm tall is placed 20 cm from:
(i) a diverging lens of focal length 40 cm.
(ii) a converging lens of focal length 40 cm.
(b) Draw labelled ray diagrams to show the formation of images in case (i) and (ii) above (The diagrams may not be according to scale).
- Name the lens which always forms an erect and virtual image.
- State whether the image in part (a) is magnified or diminished.
At what distance from a concave lens of focal length 20 cm a 6 cm tall object be placed so as to obtain its image at 15 cm from the lens? Also calculate the size of the image formed.
Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer for the above situation and label it.
A student obtained clear image of window grills on the screen. But the teacher told him to get the image of a tree far away, instead of window. To get a clear image, the lens must be ............................
Distinguish between Concave lens and Convex Lens.
A parallel, oblique beam of light falls on a concave lens. Draw a diagram to show refraction of light through the lens.
