English Medium
Academic Year: 2012-2013
Date: March 2013
Advertisements
Write two reasons responsible for late discovery of noble gases ?
Chapter: [0.05] Periodic Classification of Elements
List two measures that you would suggest for the better management of water resources.
Chapter: [0.16] Sustainable Management of Natural Resources
“Cell division is a type of reproduction in unicellular organism.” Justify.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Trace the path of sperms from where they are produced in human body to the exterior.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Write the functions of secretions of prostate gland and seminal vesicles in humans.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
A ray of light falls normally on the surface of a transparent glass slab. Draw a ray diagram to show its path and also mark angle of incidence and angle of emergence.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
List two advantages associated with water harvesting at the community level.
Chapter: [0.16] Sustainable Management of Natural Resources
We often observe domestic waste decomposing in the bylanes of our homes. List four ways to make the residents aware that the improper disposal of wastes is harmful to the environment and also for their own health.
Chapter: [0.13] Our Environment
Complete the following chemical equations: C2H5OH+O2→
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
Complete the following chemical equations : C2H5OH
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
Complete the following chemical equations : C2H5OH + Na →
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
Why homologous series of carbon compounds are so called? Write chemical formula of two consecutive members of a homologous series and state the part of these compounds that determines their (i) physical properties, and (ii) chemical properties.
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
The elements Li, Na and K, each having one valence electron, are in period 2, 3 and 4 respectively of modern periodic table.
(i) In which group of the periodic table should they be ?
(ii) Which one of them is least reactive ?
(iii) Which one of them has the largest atomic radius ? Give reason in justify your answer in each case.
Chapter: [0.05] Periodic Classification of Elements
Given below are some elements of the modern periodic table. Atomic number of the element is given in parentheses.
A(4), B(9), C(14), D(19), E(20)
(a) Select the element that has one electron in the outermost shell. Also, write the electronic configuration of this element.
(b) Which two elements amongst these belong to the same group? Give reasons for your answer.
(c) Which two elements amongst these belong to the same period? Which one of the two has bigger atomic radius?
Chapter: [0.05] Periodic Classification of Elements
Write two examples of sexually transmitted diseases caused by virus.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Write two examples of sexually transmitted diseases caused by bacteri.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Explain how the transmission of virus and bacteria diseases be prevented?
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Name the following : Thread like non-reproductive structures present in Rhizopus.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Name the following : 'Blobs' that develop at the tips of the non-reproductive threads in Rhizopus.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Name the following :
Explain the structure and the function of the structures released from the ‘blobs’ in Rhizopus.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
"The sex of a newborn child is a matter of chance and none of the parents may be considered responsible for it". Draw a flow chart showing determination of sex of a newborn to justify this statement.
Chapter: [0.08] Heredity
Advertisements
State fossils importance in the study of evolution with the help of a suitable example.
Chapter: [0.08] Heredity
An object of height 4 cm is kept at a distance of 30 cm from a concave lens. Use lens formula to determine the image distance, nature and size of the image formed if focal length of the lens is 15 cm.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Mention the types of mirrors used as (i) rear view mirrors, (ii) shaving mirrors. List two reasons to justify your answers in each case.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
State the difference in colours of the sun observed during sunrise/sunset and noon. Give explanation for each.
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
List two main components of ecosystem?
Chapter: [0.13] Our Environment
We do not clean natural ponds or lakes but an aquarium needs to be cleaned regularly. Why is it so ? Explain.
Chapter: [0.13] Our Environment
Draw a sectional view of human female reproductive system and label the following parts :
(i) Where the development of egg occurs.
(ii) Where fertilization takes place.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Describe, in brief, the changes the uterus undergoes
(i) to receive the zygote.
(ii) if zygote is not formed
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
(a) Identify A, B and C in the given diagram and write their functions.
(b) Mention the role of gamete and zygote in sexually reproducing organisms.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Draw two possible isomers of the compound with molecular formula C3H6O and write their names.
Give the electron dot structures of the above two compounds.
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
A person cannot read newspaper placed nearer than 50 cm from his eyes. Name the defect of vision he is suffering from. Draw a ray diagram to illustrate this defect. List its two possible causes. Draw a ray diagram to show how this defect may be corrected using a lens of appropriate focal length.
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
Define the term absolute refractive index. The absolute refractive index of diamond is 2.42. What is the meaning of this statement? Refractive indices of media A, B C and D are given below:
|
Media |
Refractive index |
|
A |
1.33 |
|
B |
1.44 |
|
C |
1.52 |
|
D |
1.65 |
In which of these four media is the speed of light (i) minimum and (ii) maximum ?
Find the refractive index of medium C with respect to medium B.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Select the correct statements for the process of budding in yeast:
I. A bud arises from a particular region on a parent body.
II. A parent cell divides into two daughter cells, here the parental identity is lost.
III. Before detaching from the parent body a bud may form another bud.
IV. A bud when detaches from the parent body grows into a new individual.
(A) I, II and III
(B) II, III and IV
(C) III, IV and I
(D) IV, I and II
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
A student after observing a slide showing different stages of binary fission in Amoeba draws the following diagrams. However these diagrams are not in proper sequence: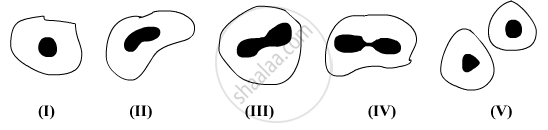
The correct sequence is:
(A) I, V, IV, III, II
(B) I, III, IV, V, II
(C) I, V, III, IV, II
(D) I, IV, V, III, II
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
In the figure, the parts marked A, B and C are sequentially:

(A) Plumule, Radicle and Cotyledon
(B) Radicle, Plumule and Cotyledon
(C) Plumule, Cotyledon and Radicle
(D) Radicle, Cotyledon and Plumule
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Study the different conclusions drawn by students of a class on the basis of observations of preserved/available specimens of plants and animals.
I. Potato and sweet potato are analogous organs in plants.
II. Wings of insects and wings of birds are homologous organs in animals.
III. Wings of insects and wings of bats are analogous organs in animals.
IV. Thorns of citrus and tendrils of cucurbita are analogous organs in plants.
The correct conclusions are:
(A) I, and II
(B) II and IV
(C) I and III
(D) III and IV
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
Advertisements
You have potato, carrot, radish, sweet potato, tomato and ginger bought from the market in your jute bag. Identify two vegetables to represent the correct homologous structures.
(A) Potato and tomato
(B) Carrot and tomato
(C) Potato and sweet potato
(D) Carrot and radish
Chapter: [0.08] Heredity
Hard water required for an experiment is not available in a school laboratory. However, following salts are available in the laboratory. Select the salts which may be dissolved in water to make it hard for the experiment.
|
(1) |
Calcium Sulphate |
(2) |
Sodium Sulphate |
|
(3) |
Calcium Chloride |
(4) |
Potassium Sulphate |
|
(5) |
Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate |
(6) |
Magnesium Chloride |
(A) 1, 2 and 4
(B) 1, 3 and 6
(C) 3, 5 and 6
(D) 2, 4 and 5
Chapter: [0.02] Acids, Bases and Salts
A student prepared 20% sodium hydroxide solution in a beaker containing water. The observations noted by him are given below.
I. Sodium hydroxide is in the form of pellets.
II. It dissolves in water readily.
III. The beaker appears cold when touched from outside.
IV. The red litmus paper turns blue when dipped into the solution.
The correct observations are:
(A) I, II, and III
(B) II, III and IV
(C) III, IV and I
(D) I, II and IV
Chapter: [0.02] Acids, Bases and Salts
Read the following statements:
I. When a red litmus paper is dipped into reaction mixture of a saponification reaction, it turns blue and the reaction is exothermic.
II. When a blue litmus paper is dipped into reaction mixture of a saponification reaction, its colour does not change and the reaction is exothermic.
III. When a red litmus paper is dipped into reaction mixture of a saponification reaction, its colour does not change and the reaction is endothermic.
IV. When a blue litmus paper is dipped into reaction mixture of a saponification reaction, its colour does not change and the reaction is endothermic.
Which of the above statements are correct:
(A) I, and II
(B) II and III
(C) III and IV
(D) I and IV
Chapter: [0.02] Acids, Bases and Salts
A student takes 2 mL acetic acid in a dry test tube and adds a pinch of sodium hydrogen carbonate to it. He makes the following observations:
I. A colourless and odourless gas evolves with a brisk effervescence.
II. The gas turns lime water milky when passed through it.
III. The gas burns with an explosion when a burning splinter is brought near it.
IV. The gas extinguishes the burning splinter that is brought near it.
The correct observations are:
(A) I, II, and III
(B) II, III and IV
(C) III, IV and I
(D) IV, I and II
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
In an experiment to study the properties of acetic acid a student takes about 2 mL of acetic acid in a dry test tube. He adds about 2 mL of water to it and shakes the test tube well. He is likely to observe that:
(A) the acetic acid dissolves readily in water
(B) the solution becomes light orange
(C) water floats over the surface of acetic acid
(D) acetic acid floats over the surface of water
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
A student focussed the image of a distant object using a device ‘X’ on a white screen ‘S’ as shown in the figure. If the distance of the screen from the device is 40 cm, select the correct statement about the device.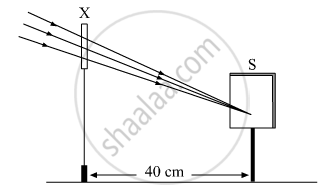
(A) The device X is a convex lens of focal length 20 cm.
(B) The device X is a concave mirror of focal length 40 cm.
(C) The device X is a convex mirror of radius of curvature 40 cm.
(D) The device X is a convex lens of focal length 40 cm.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
A student obtained a sharp image of a burning candle, placed at the farther end of a laboratory table, on a screen using a concave mirror. For getting better value of focal length of the mirror, the subject teacher suggested him for focusing a well illuminated distant object. What should the student do?
(A) He should move the mirror away from the screen.
(B) He should move the mirror slightly towards the screen.
(C) He should move the mirror as well as the screen towards the newly selected object.
(D) He should move only the screen towards the newly selected object.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Out of the five incident rays shown in the figure find the three rays that are obeying the laws of refraction and may be used for locating the position of image formed by a convex lens: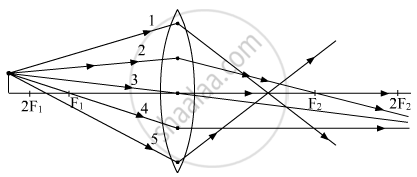
(A) 1, 2 and 3
(B) 2, 3 and 4
(C) 3, 4 and 5
(D) 1, 2 and 4
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
The diagrams showing the correct path of the ray after passing through the lens are:
 |
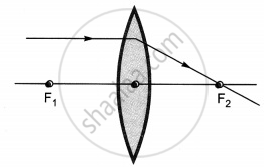 |
| I | II |
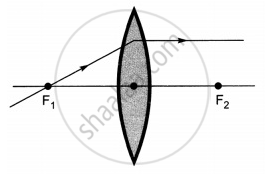 |
 |
| III | IV |
II and III only
I and II only
I, II and III
I, II and IV
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
While performing the experiment to trace the path of a ray of light passing through a glass prism, four students marked the incident ray and the emergent ray in their diagrams in the manner shown below. 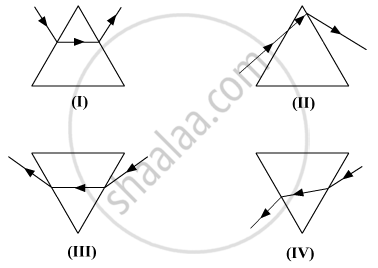
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
In an experiment to trace the path of a ray of light through a glass prism for different values of angle of incidence a student would find that the emergent ray:
(A) is parallel to the incident ray
(B) perpendicular to the incident ray
(C) is parallel to the refracted ray
(D) bends at an angle to the direction of incident ray
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
After tracing the path of rays of light through a glass slab for three different angles of incidence, a student measured the corresponding values angle of refraction r and angle of emergence e and recorded them in the table given below:
|
S. No. |
∠i |
∠i |
∠e |
|
I |
30° |
20° |
31° |
|
II |
40° |
25° |
40° |
|
III |
50° |
31° |
49° |
The correct observations are:
(A) I and II
(B) II and III
(C) I and III
(D) I, II and III
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Select from the following the best set-up for tracing the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass slab:
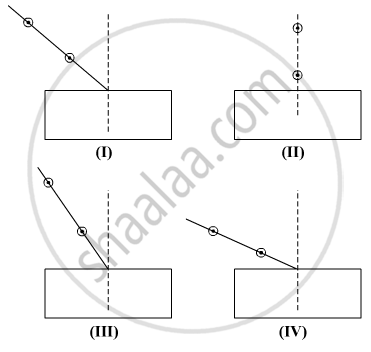
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 10 Science with solutions 2012 - 2013
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 10 Science-2013 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Science, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 10.
How CBSE Class 10 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Science will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
