Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Describe cost on the basis of behaviour.
उत्तर
- Fixed costs: Fixed costs are those costs which remain fixed in amount irrespective of changes in the volume of output during a given period of time. Such costs do not change with changes (increase or decrease) in the level of activity upto a certain limit. Rent, insurance, depreciation of plant are examples of fixed costs. The behaviour of fixed costs is shown in the following graph.
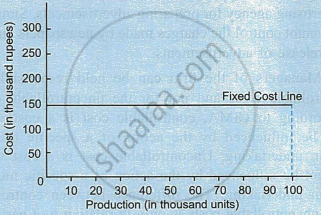
This graph shows that cost remains fixed at ₹ 1,50,000 from 0 to 1,00,000 units of output. It must be noted that fixed cost remains constant in total but fixed cost per unit of production changes with changes in the level of output. For example, when production is 30,000 units, fixed cost per unit is ₹ 5 (1,50,000 ÷ 30,000) but when production is 60,000 units, fixed cost per unit decreases to ₹ 2.5 (1,50,000 ÷ 60,000). - Variable costs: Variable costs are those costs which vary in amount with changes in the level of output or activity. Such costs increase and decrease in the same proportion in which the level of output increases or decreases. Variable costs vary in total amount but remain constant per unit of production. For example, when the level of output increases from 5,000 units to 6,000 units, the amount of variable costs increase from ₹ 25,000 to ₹ 30,000. In this case, the variable cost per unit remains unchanged at ₹ 5 (25,000 ÷ 5,000 and 30,000 ÷ 6,000). Thus, there is a linear relationship between volume of production and total variable costs. The behaviour of variable costs is shown in the graph. Sugarcane used to produce sugar is an example of variable cost.

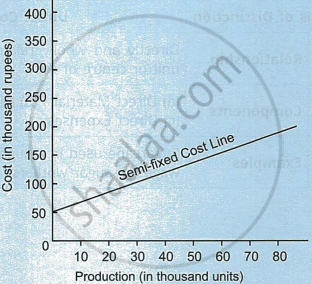
- Semi-variable cost or semi-fixed cost: Semi-fixed costs are those costs which vary but not in direct proportion to changes in the volume of production. They are a combination of fixed and variable costs. In other words, semi-fixed costs are partly fixed and partly variable. Such costs are neither perfectly fixed nor absolutely variable. The fixed component of such costs represents the cost of providing capacity and the variable component is caused by using the capacity. For example, the rent of a telephone is a fixed cost whereas the charges for calls made during a month are a variable cost. The behaviour of semi-fixed costs is shown in the following graph.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Distinguish between Fixed cost and Variable cost.
A firm has to pay a fixed rent of ₹ 500 for the postpaid mobile bill and further pay extra charges for the calls made in a month. Identify the type of cost mentioned here.
Indirect material scrap is adjusted along with ______.
Overheads are often related to accounting concepts such as fixed cost and ______ cost.
Variable cost is a cost that ______.
The cost remains same at all levels of output is called ______ cost.
It refers to the expenses incurred on those items which are not directly chargeable to production. Salaries of timekeeper, foremen and watchmen are examples of this cost. This cost is incurred for the concern as a whole rather than a particular product.
Which definition best describes indirect costs?
Which of the following best describes a fixed cost?
Fixed cost is a cost which remains same at ______.
What is meant by sunk cost?
Distinguish between shut down cost and sunk cost.
Distinguish between Direct Labour cost and Indirect Labour cost.
Fixed cost is a cost which ______.
Fixed cost per unit decreases when ______.
"Some costs are semi-variable in nature." Comment.
Classify cost according to its nature.
Explain with an example, the meaning of variable costs.
