Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Describe various forms of lipid with a few examples.
उत्तर
Lipids are generally water-insoluble. They could be simple fatty acids. A fatty acid has a carboxyl group attached to an R-group. The R-group could be a methyl (–CH3), or ethyl (–C2H5) or a higher number of CH2 groups (1 carbon to 19 carbons). For example, palmitic acid has 16 carbons including carboxyl carbon. Arachidonic acid has 20 carbon atoms including carboxyl carbon. Fatty acids could be saturated (without a double bond) or unsaturated (with one or more C=C double bonds). Another simple lipid is glycerol which is trihydroxy propane.
- Many lipids have both glycerol and fatty acids. Here the fatty acids are found esterified with glycerol. They can be then monoglycerides,
diglycerides and triglycerides. These are also called fats and oils based on melting point. Oils have a lower melting point (e.g., gingerly oil) and hence remain as oil in winter. - Some lipids have phosphorous and a phosphorylated organic compound in them. These are phospholipids. They are found in cell membranes. Lecithin is one example. Some tissues especially the neural tissues have lipids with more complex structures.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Attempt titrating an amino acid against a weak base and discover the number of dissociating ( ionizable ) functional groups in the amino acid.
Draw the structure of the amino acid, alanine.
The acid insoluble fraction does not contain
Identify the incorrect statement :
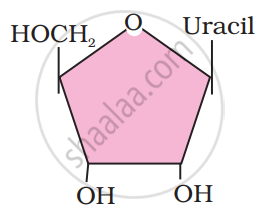
Identify the structural formula given in the figure.
Aminoacids, have both an amino group and a carboxyl group in their structure. Which one of the following is an amino acid?
An aminoacid under certain conditions have both positive and negative charges simultaneously in the same molecule. Such a form of aminoacid is called ______.
Write the name of anyone aminoacid, sugar, nucleotide and fatty acid.
Glycine and Alanine are different with respect to one substituent on the α-carbon. What are the other common substituent groups?
What is the difference between a nucleotide and nucleoside? Give two examples of each with their structure.
