Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Biological Classification
3: Plant Kingdom
4: Animal Kingdom
5: Morphology of Flowering Plants
6: Anatomy of Flowering Plants
7: Structural Organisation in Animals
8: Cell : the Unit of Life
▶ 9: Biomolecules
10: Cell Cycle and Cell Division
11: Transport in Plants
12: Mineral Nutrition
13: Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
14: Respiration in Plants
15: Plant Growth and Development
16: Digestion and Absorption
17: Breathing and Exchange of Gases
18: Body Fluids and Circulation
19: Excretory Products and Their Elimination
20: Locomotion and Movement
21: Neural Control and Coordination
22: Chemical Coordination and Integration
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 11 chapter 9 - Biomolecules NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 11 chapter 9 - Biomolecules - Shaalaa.com](/images/biology-english-class-11_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 9: Biomolecules
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 9 of CBSE NCERT Exemplar for Biology [English] Class 11.
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 11 9 Biomolecules Exercises [Pages 43 - 48]
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
It is said that elemental composition of living organisms and that of inanimate objects (like earth’s crust) are similar in the sense that all the major elements are present in both. Then what would be the difference between these two groups? Choose a correct answer from among the following:
Living organisms have more gold in them than inanimate objects
Living organisms have more water in their body than inanimate objects
Living organisms have more carbon, oxygen and hydrogen per unit mass than inanimate objects
Living organisms have more calcium in them than inanimate objects
Many elements are found in living organisms either free or in the form of compounds. Which of the following is not found in living organisms?
Silicon
Magnesium
Iron
Sodium
Aminoacids, have both an amino group and a carboxyl group in their structure. Which one of the following is an amino acid?
Formic acid
Glycerol
Glycolic Acid
Glycine
An aminoacid under certain conditions have both positive and negative charges simultaneously in the same molecule. Such a form of aminoacid is called ______.
Acidic form
Basic form
Aromatic form
Zwitterionic form
Sugars are technically called carbohydrates, referring to the fact that their formulae are only multiple of C(H2O). Hexoses therefore have six carbons, twelve hydrogens and six oxygen atoms. Glucose is a hexose. Choose from among the following another hexose.
Fructose
Erythrose
Ribulose
Ribose
When you take cells or tissue pieces and grind them with an acid in a mortar and pestle, all the small biomolecules dissolve in the acid. Proteins, polysaccharides and nucleic acids are insoluble in mineral acid and get precipitated. The acid soluble compounds include aminoacids, nucleosides, small sugars etc. When one adds a phosphate group to a nucleoside, one gets another acid soluble biomolecule called ______.
Nitrogen base
Adenine
Sugar phosphate
Nucleotide
When we homogenise any tissue in an acid the acid soluble pool represents ______.
Cytoplasm
Cell membrane
Nucleus
Mitochondria
The most abundant component of living organisms is ______.
Protein
Water
Sugar
Nucleic acid
A homopolymer has only one type of building block called monomer repeated ‘n’ number of times. A heteropolymer has more than one type of monomer. Proteins are heteropolymers usually made of ______.
20 types of monomers
40 types of monomers
30 types of monomers
Only one type of monomer
Proteins perform many physiological functions. For example some functions as enzymes. One of the following represents an additional function that some proteins discharge?
Antibiotics
Pigment conferring colour to the skin
Pigments making colours of flowers
Hormones
Glycogen is a homopolymer made of ______.
Glucose units
Galactose units
Ribose units
Aminoacids
The number of ‘ends’ in a glycogen molecule would be ______.
Equal to the number of branches plus one
Equal to the number of branch points
One
Two, one on the left side and another on the right side
The primary structure of a protein molecule has ______.
Two ends
One end
Three ends
No ends
Enzymes are biocatalysts. They catalyse biochemical reactions. In general they reduce activation energy of reactions. Many physico-chemical processes are enzyme mediated. Which of the following reactions is not engyme-mediated in biological system?
Dissolving CO2 in water
Untwining the two strands of DNA
Hydrolysis of sucrose
Formation of peptide bond
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Medicines are either man made (i.e., synthetic) or obtained from living organisms like plants, bacteria, animals etc. and hence the latter are called natural products. Sometimes natural products are chemically altered by man to reduce toxicity or side effects. Write against the following whether they were initially obtained as a natural product or as a synthetic chemical.
Penicillin ______
Natural product
Synthetic chemical
Medicines are either man made (i.e., synthetic) or obtained from living organisms like plants, bacteria, animals etc. and hence the latter are called natural products. Sometimes natural products are chemically altered by man to reduce toxicity or side effects. Write against the following whether they were initially obtained as a natural product or as a synthetic chemical.
Sulfonamide ______
Natural product
Synthetic chemical
Medicines are either man made (i.e., synthetic) or obtained from living organisms like plants, bacteria, animals etc. and hence the latter are called natural products. Sometimes natural products are chemically altered by man to reduce toxicity or side effects. Write against the following whether they were initially obtained as a natural product or as a synthetic chemical.
Vitamin C ______
Natural product
Synthetic chemical
Medicines are either man made (i.e., synthetic) or obtained from living organisms like plants, bacteria, animals etc. and hence the latter are called natural products. Sometimes natural products are chemically altered by man to reduce toxicity or side effects. Write against the following whether they were initially obtained as a natural product or as a synthetic chemical.
Growth Hormone ______
Natural product
Synthetic chemical
Select an appropriate chemical bond among ester bond, glycosidic bond, peptide bond and hydrogen bond and write against the following.
Polysaccharide ______
Ester bond
Glycosidic bond
Peptide bond
Hydrogen bond
Select an appropriate chemical bond among ester bond, glycosidic bond, peptide bond and hydrogen bond and write against the following.
Protein ______
Ester bond
Glycosidic bond
Peptide bond
Hydrogen bond
Select an appropriate chemical bond among ester bond, glycosidic bond, peptide bond and hydrogen bond and write against the following.
Fat ______
Ester bond
Glycosidic bond
Peptide bond
Hydrogen bond
Select an appropriate chemical bond among ester bond, glycosidic bond, peptide bond and hydrogen bond and write against the following.
Water ______
Ester bond
Glycosidic bond
Peptide bond
Hydrogen bond
Write the name of anyone aminoacid, sugar, nucleotide and fatty acid.
Reaction given below is catalysed by oxidoreductase between two substrates A and A’, complete the reaction.
A reduced + A’ oxidised `→`
How are prosthetic groups different from co-factors?
Glycine and Alanine are different with respect to one substituent on the α-carbon. What are the other common substituent groups?
Starch, Cellulose, Glycogen, Chitin are polysaccharides found among the following. Choose the correct answer:
Cotton fibre ______
Starch
Cellulose
Glycogen
Chitin
Starch, Cellulose, Glycogen, Chitin are polysaccharides found among the following. Choose the correct answer:
Exoskeleton of cockroach ______
Starch
Cellulose
Glycogen
Chitin
Starch, Cellulose, Glycogen, Chitin are polysaccharides found among the following. Choose the correct answer:
Liver ______
Starch
Cellulose
Glycogen
Chitin
Starch, Cellulose, Glycogen, Chitin are polysaccharides found among the following. Choose the correct answer:
Peeled potato ______
Starch
Cellulose
Glycogen
Chitin
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Enzymes are proteins. Proteins are long chains of aminoacids linked to each other by peptide bonds. Aminoacids have many functional groups in their structure. These functional groups are, many of them at least, ionisable. As they are weak acids and bases in chemical nature, this ionization is influenced by pH of the solution. For many enzymes, activity is influenced by surrounding pH. This is depicted in the curve below, explain briefly.
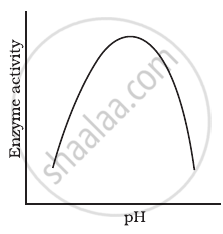
Is rubber a primary metabolite or a secondary metabolite? Write four sentences about rubber.
Schematically represent primary, secondary and tertiary structures of a hypothetical polymer say for example a protein.
Nucleic acids exhibit secondary structure, justify with example.
Comment on the statement “living state is a non-equilibrium steady- state to be able to perform work”.
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Formation of enzyme-substrate complex (ES) is the first step in catalysed reactions. Describe the other steps till the formation of product.
What are different classes of enzymes? Explain any two with the type of reaction they catalyse.
Nucleic acids exhibit secondary structure. Describe through Wetson- Crick Model.
What is the difference between a nucleotide and nucleoside? Give two examples of each with their structure.
Describe various forms of lipid with a few examples.
Solutions for 9: Biomolecules
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 11 chapter 9 - Biomolecules NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 11 chapter 9 - Biomolecules - Shaalaa.com](/images/biology-english-class-11_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 11 chapter 9 - Biomolecules
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Biology [English] Class 11 CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics Biology [English] Class 11 CBSE 9 (Biomolecules) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT Exemplar textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Biology [English] Class 11 chapter 9 Biomolecules are How to Analyse Chemical Composition?, Primary and Secondary Metabolites, Biomacromolecules, Polysaccharides, Proteins, Nucleic Acids, Structure of Proteins, Nature of Bond Linking Monomers in a Polymer, Enzymes, Enzymes - Chemical Reactions, Enzymes - High Rates of Chemical Conversions, Nature of Enzyme Action, Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity, Classification and Nomenclature of Enzymes, Enzymes - Co-factors, Dynamic State of Body Constituents – Concept of Metabolism, Metabolic Basis for Living, The Living State, Biomolecules in Living System, Chemical Constituents of Living Cells, Carbohydrates, Structure and Function of Lipids.
Using NCERT Exemplar Biology [English] Class 11 solutions Biomolecules exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Exemplar Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Biology [English] Class 11 students prefer NCERT Exemplar Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 9, Biomolecules Biology [English] Class 11 additional questions for Mathematics Biology [English] Class 11 CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
