Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Biological Classification
3: Plant Kingdom
4: Animal Kingdom
5: Morphology of Flowering Plants
6: Anatomy of Flowering Plants
7: Structural Organisation in Animals
8: Cell : the Unit of Life
9: Biomolecules
10: Cell Cycle and Cell Division
▶ 11: Transport in Plants
12: Mineral Nutrition
13: Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
14: Respiration in Plants
15: Plant Growth and Development
16: Digestion and Absorption
17: Breathing and Exchange of Gases
18: Body Fluids and Circulation
19: Excretory Products and Their Elimination
20: Locomotion and Movement
21: Neural Control and Coordination
22: Chemical Coordination and Integration
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 11 chapter 11 - Transport in Plants NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 11 chapter 11 - Transport in Plants - Shaalaa.com](/images/biology-english-class-11_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 11: Transport in Plants
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 11 of CBSE NCERT Exemplar for Biology [English] Class 11.
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 11 11 Transport in Plants Exercises [Pages 54 - 62]
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Which of the following statements does not apply to reverse osmosis?
It is used for water purification
In this technique, pressure greater than osmotic pressure is applied to the system
It is a passive process
It is an active process
Which one of the following will not directly affect transpiration?
Temperature
Light
Wind speed
Chlorophyll content of leaves
The lower surface of leaf will have more number of stomata in a ______.
Dorsiventral leaf
Isobilateral leaf
Both dorsiventral leafand isobilateral leaf
None of the above
The form of sugar transported through phloem is ______.
Glucose
Fructose
Sucrose
Ribose
The process of guttation takes place ______.
When the root pressure is high and the rate of transpiration is low
When the root pressure is low and the rate of transpiration is high
When the root pressure equals the rate of transpiration
When the root pressure as well as rate of transpiration are high
Which of the following is an example of imbibition?
Uptake of water by root hair
Exchange of gases in stomata
Swelling of seed when put in soil
Opening of stomata
When a plant undergoes senescence, the nutrients may be ______.
Accumulated
Withdrawn
Translocated
None of the above
Water potential of pure water at standard temperature is equal to ______.
10
20
Zero
None of the above
Mycorrhiza is a symbiotic association of fungus with root system which helps in ______.
- Absorption of water
- Mineral nutrition
- Translocation
- Gaseous exchange
Only Absorption of water
Only Mineral nutrition
Both Absorption of water and Mineral nutrition
Both Mineral nutrition and Translocation
Based on the figure given below which of the following statements is not correct?
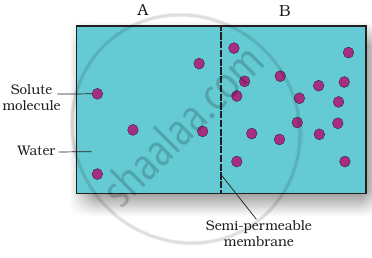
Movement of solvent molecules will take place from chamber A to B.
Movement of solute will take place from A to B.
Presence of a semipermeable is a pre-requisite for this process to occur.
The direction and rate of osmosis depends on both the pressure gradient and concentration gradient.
Match the following and choose the correct option
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Leaves | i. Anti-transpirant |
| B. Seed | ii. Transpiration |
| C. Roots | iii. Negative osmotic potential |
| D. Aspirin | iv. Imbibition |
| E. Plasmolyzed cell | v. Absorption |
A - ii, B - iv, C - v, D - i, E - iii
A - iii, B - ii, C - iv, D - i, E - v
A - i, B - ii, C - iii, D - iv, E - v
A - v, B - iv, C - iii, D - ii, E - i
Mark the mismatched pair.
Amyloplast: store protein granule
Elaioplast: store oils or fats
Chloroplasts: contain chlorophyll pigments
Chromoplasts: contain coloured pigments other than chlorophyll
Leucoplast: contains colourless pigments
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Smaller, lipid soluble molecules diffuse faster through cell membrane, but the movement of hydrophilic substances are facilitated by certain transporters which are chemically ______.
In a passive transport across a membrane, when two different molecules move in opposite direction and independent of each other, it is called as ______.
Osmosis is a special kind of diffusion, in which water diffuses across the cell membrane. The rate and direction of osmosis depends upon both ______.
A flowering plant is planted in an earthen pot and irrigated. Urea is added to make the plant grow faster, but after some time the plant dies. This may be due to ______.
Absorption of water from soil by dry seeds increases the ______ thus helping seedlings to come out of soil.
Water moves up against gravity and even for a tree of 20m height, the tip receives water within two hours. The most important physiological phenomenon which is responsible for the upward movement of water is ______.
The plant cell cytoplasm is surrounded by both cell wall and cell membrane. The specificity of transport of substances are mostly across the cell membrane, because ______.
The C4 plants are twice as efficient as C3 plants in terms of fixing CO2 but lose only ______ as much water as C3 plants for the same amount of CO2 fixed.
In a plant, tranalocation in xylem is unidirectional while in phloem it is bidirectional. Explain.
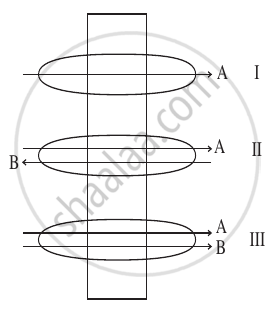
Identify the process occurring in I, II and III
Given below is a table. Fill in the gaps
| Property | Simple diffusion | Facilitated transport | Active Transport |
| i Highly selective | ______ | Yes | ______ |
| ii Uphill transport | ______ | ______ | Yes |
| iii Requires ATP | ______ | ______ | ______ |
Define water potential and solute potential.
Why is solute potential always negative? Explain yw = ys + yp
Tradescantia leaf epidermal peel was taken and
- Placed in salt solution for five minutes.
- After that it was placed in distilled water.
When seen under the microscope what would be observed in a and b?
Differentiate between Apoplast and Symplast pathways of water movement. Which of these would need active transport?
How does water moves within the root?
Give the location of casparian strip and explain its role in the water movement.
Differentiate between guttation and transpiration.
Transpiration is a necessary evil in plants. Explain.
Describe briefly the three physical properties of water which helps in ascent of water in xylem.
A gardener forgot to water a potted plant for a day during summer, what will happen to the plant? Do you think it is reversible? If yes, how?
Identify a type of molecular movement which is highly selective and requires special membrane proteins, but does not require energy.
Correct the statements:
Cells shrink in hypotonic solutions and swell in hypertonic solutions.
Correct the statements:
Imbibition is a special type of diffusion when water is absorbed by living cells.
Correct the statements:
Most of the water flow in the roots occurs via the symplast.
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Minerals absorbed by the roots travel up the xylem. How do they reach the parts where they are needed most? Do all the parts of the plant get the same amount of the minerals?
If one wants to find minerals and in the form they are mobilised in the plant, how will an analysis of the exudate help?
From your knowledge of physiology can you think of some method of increasing the life of cut plants in a vase?
Do different species of plants growing in the same area show the same rate of transpiration at a particular time? Justify your answer.
Water is indispensable for life. What properties of water make it useful for all biological processes on the earth?
How is the intracellular levels of ions maintained higher than extracellular levels in animal cells?
Cut pieces of beetroot do not leave colour in cold water but do so in hot water. Explain.
In a girdled plant, when water is supplied to the leaves above the girdle, leaves may remain green for sometime then wilt and ultimately die. What does it indicate?
Various types of transport mechanisms are needed to fulfil the mineral requirements of a plant. Why are they not fulfilled by diffusion alone?
How can plants be grown under limited water supply without compromising on metabolic activities?
Will the ascent of sap be possible without the cohesion and adhesion of the water molecules? Explain.
Keep some freshly cut flowers in a solution of food colour. Wait for sometime for the dye to rise in the flower, when the stem of the flower is held up in light, coloured strands can be seen inside. Can this experiment demonstrate which tissue is conducting water up the stem?
When a freshly collected Spirogyra filament is kept in a 10% potassium nitrate solution, it is observed that the protoplasm shrinks in size:
What is this phenomenon called?
When a freshly collected Spirogyra filament is kept in a 10% potassium nitrate solution, it is observed that the protoplasm shrinks in size:
What will happen if the filament is replaced in distilled water?
Sugar crystals do not dissolve easily in ice cold water. Explain.
Salt is applied to tennis lawns to kill weeds. How does salting tennis lawns help in killing of weeds without affecting the grass?
What is the chemical composition of xylem and phloem sap?
Observe the figure and answer the question provided below the figure.

Why does tube B show higher water rise than A?
What are ‘aquaporins’? How does presence of aquaporins affect osmosis?
ABA (Abscisic acid) is called a stress hormone. How does this hormone overcome stress conditions?
ABA (Abscisic acid) is called a stress hormone. From where does this hormone get released in leaves?
We know that plants are harmed by excess water. But plants survive under flooded condition. How are they able to manage excess water?
Differentiate between diffusion and translocation in plants.
How is facilitated diffusion different from diffusion?
Explain the mass flow hypothesis of transport in phloem.
Observe the diagram and answer the following;
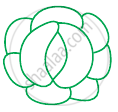 (i) |
 (ii) |
- Are these types of guard cells found in monocots or dicots?
- Which of these shows a higher water content (i) or (ii)?
- Which element plays an important role in the opening and closing of stomata?
Define Uniport, Symport and Antiport. Do they require energy?
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Minerals are present in the soil in sufficient amounts. Do plants need to adjust the types of solutes that reach the xylem? Which molecules help to adjust this? How do plants regulate the type and quantity of solutes that reach xylem?
Plants show temporary and permanent wilting. Differentiate between the two. Do any of them indicate the water status of the soil?
Why are natural membranes selectively permeable. Give examples.
Halophytes may show cell pressure very much higher than atmospheric pressure. Explain how this can happen?
The radio labelled carbon in carbon dioxide supplied to potato plants in an experiment was seen in the tuber eventually. Trace the movement of the labelled carbon dioxide.
Water molecule is very polar. Polar end of molecule attracts opposite charges on another water molecule (acts like magnet). How will you explain this property of water with reference to upward movement of water? Comment on the upward movement of water given the intermolecular hydrogen bonding in water.
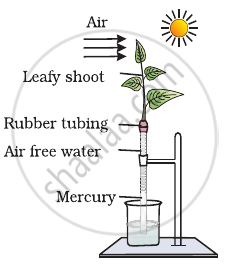
Comment on the experimental setup
- What does the setup demonstrate?
- What will happen to the level of water if a blower is placed close to setup.
- Will the mercury level fluctuate (go up/down) if phenyl mercuric acetate is sprayed on leaves?
Solutions for 11: Transport in Plants
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 11 chapter 11 - Transport in Plants NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 11 chapter 11 - Transport in Plants - Shaalaa.com](/images/biology-english-class-11_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 11 chapter 11 - Transport in Plants
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Biology [English] Class 11 CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics Biology [English] Class 11 CBSE 11 (Transport in Plants) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT Exemplar textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Biology [English] Class 11 chapter 11 Transport in Plants are Introduction of Transport in Plants, Movement of Water, Gases and Nutrients, Cell to Cell Transport, Simple Diffusion, Facilitated Diffusion, Active Transport, Comparison of Different Transport Processes, Concept of Plant-water Relations, Water Potential (ψ), Osmosi, Turgidity and Flaccidity (Plasmolysis), Concept of Imbibition, Introduction of Long Distance Transport of Water, Plants Absorb Water, Water Movement up a Plant, Transpiration, Transpiration - Transpiration and Photosynthesis – a Compromise, Uptake of Mineral Ions, Transport of Mineral Ions, Phloem Transport - Flow from Source to Sink, Phloem Transport - Pressure Flow Or Mass Flow Hypothesis, Diffusion of Gases, Transport in Plants (Numericals), Structure of Stomatal Apparatus.
Using NCERT Exemplar Biology [English] Class 11 solutions Transport in Plants exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Exemplar Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Biology [English] Class 11 students prefer NCERT Exemplar Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 11, Transport in Plants Biology [English] Class 11 additional questions for Mathematics Biology [English] Class 11 CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
