Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Biological Classification
3: Plant Kingdom
4: Animal Kingdom
5: Morphology of Flowering Plants
6: Anatomy of Flowering Plants
7: Structural Organisation in Animals
8: Cell : the Unit of Life
9: Biomolecules
10: Cell Cycle and Cell Division
11: Transport in Plants
12: Mineral Nutrition
13: Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
14: Respiration in Plants
15: Plant Growth and Development
16: Digestion and Absorption
17: Breathing and Exchange of Gases
18: Body Fluids and Circulation
▶ 19: Excretory Products and Their Elimination
20: Locomotion and Movement
21: Neural Control and Coordination
22: Chemical Coordination and Integration
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 11 chapter 19 - Excretory Products and Their Elimination NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 11 chapter 19 - Excretory Products and Their Elimination - Shaalaa.com](/images/biology-english-class-11_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 19: Excretory Products and Their Elimination
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 19 of CBSE NCERT Exemplar for Biology [English] Class 11.
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 11 19 Excretory Products and Their Elimination Exercises [Pages 108 - 113]
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
The following substances are the excretory products in animals. Choose the least toxic form among them?
Urea
Uric acid
Ammonia
Carbon dioxide
Filtration of the blood takes place at ______.
PCT
DCT
Collecting ducts
Malpighian body
Which of the following statements is correct?
ADH – prevents conversion of angiotensinogen in blood to angiotensin
Aldosterone – facilitates water reabsorption
ANF – enhances sodium reabsorption
Renin – causes vasodilation
Which of the following is removed from our body by lungs?
CO2 only
H2O only
CO2 and H2O
Ammonia
The pH of human urine is approximately ______.
6.5
7
6
7.5
Different types of excretory structures and animals are given below. Match them appropriately and mark the correct answer from among those given below:
| Excretory structure/ organ | Animals |
| A. Protonephridia | i. Prawn |
| B. Nephridia | ii. Cockroach |
| C. Malpighian tabules | iii. Earthworm |
| D. Green gland or Antennal gland | iv. Flatworms |
A - iv, B - iii, C - ii, D - i
A - iii, B - i, C - iv, D - ii
A - iii, B - iv, C - ii, D - i
A - iii, B - iv, C - ii, D - i
Which one of the following statements is incorrect?
Birds and land snails are uricotelic animals
Mammals and frogs are ureotelic animals
Aquatic amphibians and aquatic insects are ammonotelic animals
Birds and reptiles are ureotelic
Which of the following pairs is wrong?
Uricotelic ---------- Birds
Ureotelic ---------- Insects
Ammonotelic ---------- Tadpole
Ureotelic ---------- Elephant
Which one of the following statements is incorrect?
The medullary zone of kidney is divided into a few conical masses called medullary pyramids projecting into the calyces.
Inside the kidney the cortical region extends in between the medullary pyramids as renal pelvis.
Glomerulus alongwith Bowman’s capsule is called the renal corpuscle.
Renal corpuscle, proximal convoluted tabule (PCT) and distal convoluted tubule (DCT) of the nephron are situated in the cortical region of kidney.
The condition of accumulation of urea in the blood is termed as ______.
Renal Calculi
Glomerulonephritis
Uremia
Ketonuria
Which one of the following is also known as antidiuretic hormone?
Oxytocin
Vasopressin
Adrenaline
Calcitonin
Match the terms given in Column I with their physiological processes given in Column II and choose the correct answer
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Proximal convoluted tubule | i. Formation of concentrated urine |
| B. Distal convoluted tubule | ii. Filtration of blood |
| C. Henle's loop | iii. Reabsorption of 70 - 80% of electrolytes |
| D. Counter-current mechanism | iv. Ionic balance |
| E. Renal corpuscle | v. Maintenance of concentration gradient in medulla |
A - iii, B - v, C - iii, D - ii, E - i
A - iii, B - iv, C - i, D - v, E - ii
A - i, B - iii, C - ii, D - v, E - iv
A - iii, B - i, C - iv, D - v, E - ii
Match the abnormal conditions given in Column A with their explanations given in Column B and Choose the correct option
| Column A | Column B |
| A. Glycosuria | i. Accumulation of uric acid in joints |
| B. Renal calculi | ii. Inflammation in glomeruli |
| C. Glomerular nephritis | iii. Mass of crystallised salts within the kidney |
| D. Gout | iv. Presence of glucose in urine |
A - i, B - iii, C - ii, D - iv
A - iii, B - ii, C - iv, D - i
A - iv, B - iii, C - ii, D - i
A - iv, B - ii, C - iii, D - i
We can produce a concentrated/ dilute urine. This is facilitated by a special mechanism. Identify the mechanism.
Reabsorption from PCT
Reabsorption from Collecting Duct
Reabsorption/Secretion in DCT
Counter current mechanism in Henle’s loop/Vasa recta
Dialysing unit (artificial kidney) contains a fluid which is almost same as plasma except that it has ______.
High glucose
High urea
No urea
High uric acid
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Where does the selective reabsorption of Glomerular filtrate take place?
What is the excretory product from kidneys of reptiles?
What is the composition of sweat produced by sweat glands?
Identify the glands that perform the excretory function in prawns.
What is the excretory structure in amoeba?
The following abbreviations are used in the context of excretory functions, what do they stand for?
ANF
The following abbreviations are used in the context of excretory functions, what do they stand for?
ADH
The following abbreviations are used in the context of excretory functions, what do they stand for?
GFR
The following abbreviations are used in the context of excretory functions, what do they stand for?
DCT
Differentiate Glycosuria from Ketonuria.
What is the role of sebaceous glands?
Name two actively transported substances in Glomerular filtrate.
Mention any two metabolic disorders, which can be diagnosed by analysis of urine.
What are the main processes of urine formation?
Sort the following into actively or passively transported substances during reabsorption of GFR.
glucose, amino acids, nitrogenous wastes, Na+, water
Complete the following:
Urinary excretion = Tubular reabsorption + Tubular secretion –
Complete the following:
Dialysis fluid = Plasma –
Mention the substances that exit from the tubules in order to maintain a concentration gradient in the medullary interstitium.
Fill in the blanks appropriately
| Organ | Excretory wastes |
| a. Kidneys | ______ |
| b. Lungs | ______ |
| c. Liver | ______ |
| d. Skin | ______ |
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Show the structure of a renal corpuscle with the help of a diagram.
What is the role played by Renin-Angiotensin in the regulation of kidney function?
Aquatic animals generally are ammonotelic in nature where as terrestual forms are not. Comment.
The composition of glomerular filtrate and urine is not same. Comment.
What is the procedure advised for the correction of extreme renal failure? Give a brief account of it.
How have the terrestrial organisms adapted themselves for conservation of water?
Label the parts in the following diagram.
| Afferent arteriole Efferent arteriole Bowman’s capsule Glomerulus |
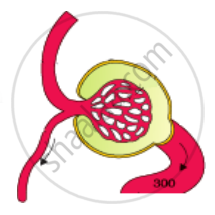 |
Explain, why a haemodialysing unit called artificial kidney?
Comment upon the hormonal regulation of selective reabsorption.
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Explain the mechanism of formation of concentrated urine in mammals.
Draw a labelled diagram showing reabsorption and secretion of major substances at different parts of the nephron.
Explain briefly, micturition and disorders of the excretory system.
How does tubular secretion help in maintaining ionic and acid-base balance in body fluids?
The glomerular filtrate in the loop of Henle gets concentrated in the descending and then gets diluted in the ascending limbs. Explain.
Describe the structure of a human kidney with the help of a labelled diagram.
Solutions for 19: Excretory Products and Their Elimination
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 11 chapter 19 - Excretory Products and Their Elimination NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 11 chapter 19 - Excretory Products and Their Elimination - Shaalaa.com](/images/biology-english-class-11_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 11 chapter 19 - Excretory Products and Their Elimination
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Biology [English] Class 11 CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics Biology [English] Class 11 CBSE 19 (Excretory Products and Their Elimination) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT Exemplar textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Biology [English] Class 11 chapter 19 Excretory Products and Their Elimination are Human Excretory System, Function of the Kidney - “Production of Urine”, Function of the Tubules, Mechanism of Concentration of the Filtrate, Regulation of Kidney Function, Micturition, Accessory Excretory Organs, Common Disorders of the Urinary System, Modes of Excretion: Ammonotelism, Ureotelism, and Uricotelism, Modes of Excretion: Ammonotelism, Ureotelism, and Uricotelism, Modes of Excretion: Ammonotelism, Ureotelism, and Uricotelism, Osmoregulation, Dialysis and Artificial Kidney, Introduction of Excretory Products and Their Elimination.
Using NCERT Exemplar Biology [English] Class 11 solutions Excretory Products and Their Elimination exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Exemplar Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Biology [English] Class 11 students prefer NCERT Exemplar Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 19, Excretory Products and Their Elimination Biology [English] Class 11 additional questions for Mathematics Biology [English] Class 11 CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
