Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Biological Classification
3: Plant Kingdom
4: Animal Kingdom
5: Morphology of Flowering Plants
6: Anatomy of Flowering Plants
7: Structural Organisation in Animals
8: Cell : the Unit of Life
9: Biomolecules
10: Cell Cycle and Cell Division
11: Transport in Plants
12: Mineral Nutrition
13: Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
▶ 14: Respiration in Plants
15: Plant Growth and Development
16: Digestion and Absorption
17: Breathing and Exchange of Gases
18: Body Fluids and Circulation
19: Excretory Products and Their Elimination
20: Locomotion and Movement
21: Neural Control and Coordination
22: Chemical Coordination and Integration
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 11 chapter 14 - Respiration in Plants NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 11 chapter 14 - Respiration in Plants - Shaalaa.com](/images/biology-english-class-11_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 14: Respiration in Plants
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 14 of CBSE NCERT Exemplar for Biology [English] Class 11.
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 11 14 Respiration in Plants Exercises [Pages 77 - 83]
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
The ultimate electron acceptor of respiration in an aerobic organisms is ______.
Cytochrome
Oxygen
Hydrogen
Glucose
Phosphorylation of glucose during glycolysis is catalysed by ______.
Phosphoglucomutase
Phosphoglucoisomerase
Hexokinase
Phosphorylase
Pyruvic acid, the key product of glycolysis can have many metabolic fates. Under aerobic condition it forms ______.
Lactic acid
CO2 + H2O
Acetyl CoA + CO2
Ethanol + CO2
Electron Transport System (ETS) is located in mitochondrial ______.
Outer membrane
Inter membrane space
Inner membrane
Matrix
Which of the following exhibits the highest rate of respiration?
Growing shoot apex
Germinating seed
Root tip
Leaf bud
Mitochondria are called powerhouses of the cell. Which of the following observations support this statement?
Mitochondria synthesise ATP
Mitochondria have a double membrane
The enzymes of the Krebs cycle are found in mitochondria
Mitochondria are found in almost all plants and animal cells
The end product of oxidative phosphorylation is ______.
NADH
Oxygen
ADP
ATP + H2O
Match the following and choose the correct option from those given below.
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Molecular oxygen | i. α - Ketoglutaric acid |
| B. Electron acceptor | ii. hydrogen acceptor |
| C. Pyruvate dehydrogenase | iii. cytochrome C |
| D. Decarboxylation | iv. acetyl Co A |
A - ii, B - iii, C - iv, D - i
A - iii, B - iv, C - ii, D - i
A - ii, B - i, C - iii, D - iv
A - iv, B - iii, C - i, D - ii
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Energy is released during the oxidation of compounds in respiration. How is this energy stored and released as and when it is needed?
Explain the term “Energy Currency”. Which substance acts as energy currency in plants and animals?
Different substrates get oxidized during respiration. How does Respiratory Quotient (RQ) indicate which type of substrate, i.e., carbohydrate, fat or protein is getting oxidized?
`R.Q. = A/B`
What do A and B stand for?
What type of substrates have R.Q. of 1, < 1 or > 1?
F1 particles participate in the synthesis of ______.
When does anaerobic respiration occur in man and yeast?
Which of the following will release more energy on oxidation? Arrange them in ascending order.
- 1 gm of fat
- 1 gm of protein
- 1 gm of glucose
- 0.5 g of protein + 0.5g glucose
The product of glycolysis (under hypoxia) in skeletal muscle and anaerobic fermentation in yeast are respectively ______ and ______.
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
If a person is feeling dizzy, glucose or fruit juice is given immediately but not a cheese sandwich Explain.
What is meant by the statement “aerobic respiration is more efficient.”?
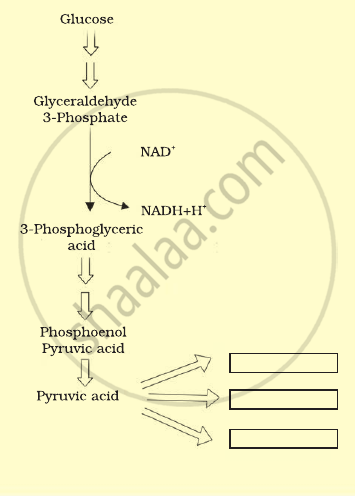
Pyruvic acid is the end product of glycolysis. What are the three metabolic products of pyruvic acid produced under aerobic and anaerobic conditions? Write their name in the space provided in the diagram.
The energy yield in terms of ATP is higher in aerobic respiration than anaerobic respiration. Why anaerobic respiration occurs even in organisms that live in aerobic condition like human beings and angiosperms?
Oxygen is an essential requirement for aerobic respiration but it enters the respiratory process at the end? Discuss.
Respiration is an energy releasing and enzymatically controlled catabolic process which involves a step-wise oxidative breakdown of organic substances inside living cells.
In this statement about respiration explain the meaning of 1) Step-wise oxidative breakdown, and 2) Organic substances (used as substrates).
Comment on the statement – Respiration is an energy producing process but ATP is being used in some steps of the process.
The figure given below shows the steps in glycolysis. Fill in the missing steps A, B, C, D and also indicate whether ATP is being used up or released at step E?

Why is respiratory pathway referred to as an amphibolic pathway? Explain.
We commonly call ATP as the energy currency of the cell. Can you think of some other energy carriers present in a cell? Name any two.
ATP produced during glycolysis is a result of substrate level phosphorylation. Explain.
Do you know any step in the TCA cycle where there is substrate level phosphorylation. Which one?
A process is occurring throughout the day, in ‘X’ organism. Cells are participating in this process. During this process ATP, CO2 and water are evolved. It is not a light dependent process.
- Name the process.
- Is it a catabolic or an anabolic process?
- What could be the raw material of this process?
When a substrate is being metabolized, why does not all the energy that released in one step. It is released in multiple steps.What is the advantage of step-wise release?
Respiration requires O2. How did the first cells on the earth manage to survive in an atmosphere that lacked O2?
It is known that red muscle fibres in animals can work for longer periods of time continuously. How is this possible?
The energy yield in terms of ATP is higher in aerobic respiration than during anaerobic respiration. Explain.
RuBP carboxylase, PEP carboxylase, Pyruvate dehydrogenase, ATPase, cytochrome oxidase, Hexokinase, Lactate dehydrogenase.
Select/choose enzymes from the list above which are involved in
- Photosynthesis
- Respiration
- Both in photosynthesis and respiration
How does a tree trunk exchange gases with the environment although it lacks stomata?
Write any two energy yielding reactions of glycolysis.
Name the site (s) of pyruvate synthesis. Also, write the chemical reaction wherein pyruvic acid dehydrogenase acts as a catalyst.
Mention the important series of events of aerobic respiration that occur in the matrix of the mitochondrion and in the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.
Respiratory pathway is believed to be a catabolic pathway. However, nature of TCA cycle is amphibolic. Explain.
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
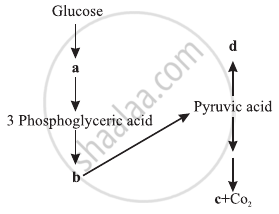
In the following flow chart, replace the symbols a,b,c and d with appropriate terms. Briefly explain the process and give any two application of it.
Given below is a diagram showing ATP synthesis during aerobic respiration, replace the symbols A, B, C, D and E by appropriate terms given in the box.

F1, Particle, Pi, 2H+, Inner mitochondrial membrane, ATP, Fo particle, ADP
Oxygen is critical for aerobic respiration. Explain its role with respect to ETS.
Enumerate the assumptions that we undertake in making the respiratory balance sheet. Are these assumptions valid for a living system? Compare fermentation and aerobic respiration in this context.
Give an account of Glycolysis. Where does it occur? What is the end product? Trace the fate of these products in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
Solutions for 14: Respiration in Plants
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 11 chapter 14 - Respiration in Plants NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 11 chapter 14 - Respiration in Plants - Shaalaa.com](/images/biology-english-class-11_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 11 chapter 14 - Respiration in Plants
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Biology [English] Class 11 CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics Biology [English] Class 11 CBSE 14 (Respiration in Plants) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT Exemplar textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Biology [English] Class 11 chapter 14 Respiration in Plants are Respiration in Plant, Plants Breathe, Phases of Respiration: Glycolysis, Phases of Respiration: Fermentation, Oxidation of Pyruvate, Types of Respiration: Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration, Phases of Respiration: Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle Or Kreb’s Cycle), Phases of Respiration: Electron Transport System (Ets) and Oxidative Phosphorylation, Respiratory Balance Sheet, Amphibolic Pathways, Respiratory Quotient (R.Q.), Exchange of Gases - in Plants, Energy Relations - Number of ATP Molecules Generated, Respiration in Plant.
Using NCERT Exemplar Biology [English] Class 11 solutions Respiration in Plants exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Exemplar Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Biology [English] Class 11 students prefer NCERT Exemplar Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 14, Respiration in Plants Biology [English] Class 11 additional questions for Mathematics Biology [English] Class 11 CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
