Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the mechanism of formation of concentrated urine in mammals.
उत्तर
The ability to produce concentrated urine is seen in mammals. The Henle's loop and Vasa recta play an important role in this.
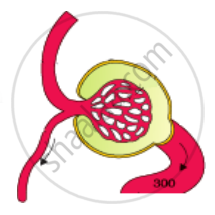
Counter Current Mechanism: The flow of filtrate in two limbs of Henle’s loop is in opposite direction. This forms a counter current. Similarly, the flow of blood through two limbs of the vasa recta also produces a counter current. The proximity between Henle’s loop and vasa recta and also the counter-current in them help in maintaining an increasing osmolarity towards the inner medullary interstitium. Thus, osmolarity increases from 300 mOsmol/L in the cortex to about 1200 mOsmol/Lin in the inner medulla.
Role of NaCl and Urea: The osmotic gradient is mainly caused by NaCl and urea. NaCl is transported by the ascending limb of Henle’s loop. NaCl is exchanged with the descending limb of the vasa recta. After that, NaCl is returned into the interstitium by the ascending limb of the vasa recta. A small amount of urea enters the ascending limb of Henle’s loop and is transported back to the interstitium by the collecting tubule.
Effect of Osmotic Gradient: The presence of an osmotic gradient in the interstitium helps the water to easily exit from the collecting tubule. This results in an increased concentration of urine. So, compared to the initial filtrate; human urine is nearly four times more concentrated.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Give a brief account of the counter current mechanism.
Which one of the following correctly explains the function of a specific part of a human nephron?
Counter current mechanism observed in the renal medulla helps in the formation of ______.
Name two actively transported substances in Glomerular filtrate.
Label the parts in the following diagram.
| Afferent arteriole Efferent arteriole Bowman’s capsule Glomerulus |
 |
Describe the structure of a human kidney with the help of a labelled diagram.
