Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
उत्तर
When an oscillatory system is made to oscillate under the action of an externally applied periodic force, it is said to execute forced vibrations. In this case the external frequency may or may not be equal to the natural frequency of the body.
In case of resonance, the externally applied periodic force has the same frequency as the natural frequency of oscillation of the given oscillatory system.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
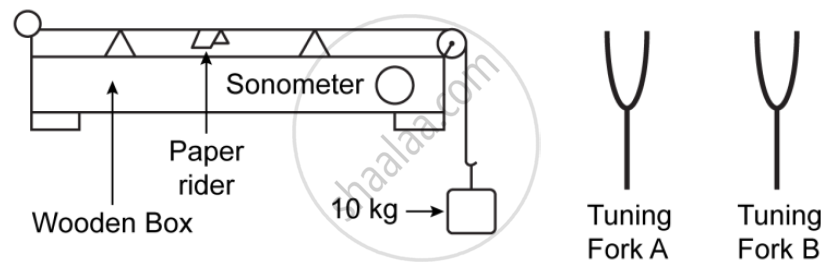
The diagram above shows a wire stretched over a sonometer. Stems of two vibrating tuning forks A and Bare touched to the wooden box of the sonometer. It is observed that the paper rider (a small piece of paper folded at the centre) present on the wire flies off when the stem of vibrating tuning fork B is touched to the wooden box but the paper just vibrates when the stem of vibrating tuning fork A is touched to the wooden box.
1) Name the phenomenon when the paper rider just vibrates.
2) Name the phenomenon when the paper rider flies off.
3) Why does the paper rider fly off when the stem of tuning fork B is touched to the box?
Describe a simple experiment to illustrate the phenomenon of resonance and explain it.
Differentiate between the following:
Free and forced vibrations.
Explain why stringed musical instruments, like the guitar, are provided with a hollow box.
The rearview mirror of a motorbike starts vibrating violently at some particular speed of the motorbike. What is the name of the phenomenon taking place? Why does the happen?
The rearview mirror of a motorbike starts vibrating violently at some particular speed of the motorbike, what could be done to stop the violent vibrations.
Explain a tuning fork (vibrating) is held close to ear. One hears a faint sound. The same vibrating tuning fork is placed on table, such that its handle is in contact with table, one hears a loud sound.
What do you understand by free (or natural) vibrations?
