Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
![Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 3 - Sound Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 3 - Sound - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-part-2-english-class-10-icse_6:39af211da77c495e91d1cf4305988990.PNG)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 3: Sound
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 3 of CISCE Frank for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE.
Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 3 Sound Exercise 3.1 i [Page 135]
How does the velocity of a wave vary with temperature?
Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 3 Sound Exercise 3.1 ii [Page 136]
Explain how the principle of echo is used by
The bat during its flight at
Explain how the principle of echo is used by
The dolphin to locate small fish as its prey
What is 'SONAR'?
State the principle on which SONAR is based.
Distinguish between compression and rarefaction.
Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 3 Sound Exercise 3.2 i [Page 145]
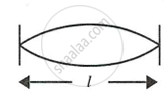
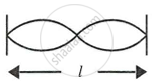
Fig. shows three ways in which a string of length l in an instrument can vibrate.
 |
 |
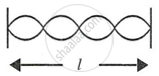 |
| (i) | (ii) | (iii) |
- Which of the diagram shows the principle note?
- Which vibration has the frequency four times that of the first?
- Which vibration is of the longest wavelength?
- What is the ratio of the frequency of the vibration in (i) and (ii)?
When a troop crosses a suspension bridge, the soldiers are asked to break steps. Explain the reason.
How does the medium affect the amplitude of free/natural vibrations of a body?
Is pitch same as frequency?
What adjustments would you make for tuning a stringed instrument for it to emit a note of a desired frequency?
Explain why strings of different thicknesses are provided on a stringed instrument.
[Hint: Natural frequency of vibration of a stretched string is inversely proportional to the radius (or thickness) of string so notes of different frequencies can be produces by vibrating different strings.]
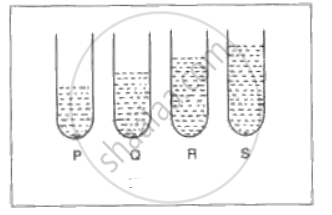
In fig. , P, Q, R and S represent test tubes each of height 20 cm which are filled with water upto heights of 10 cm, 14 cm, 16 cm and 18 cm respectively. If a vibrating tuning fork is placed over the mouth of test tube Q, a loud sound is heard.
(i) Describe the observations with the tubes P, R and S.
(ii) Give the reason for your observation in each case.
(iii) State the principle illustrated by the above experiment.
Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 3 Sound Exercise 3.2 ii [Page 146]
In fig. shows two tuning forks P and Q of the same frequency mounted on separate sound boxes with their open ends facing each other. The fork A is set into vibration. (i) Describe your observation. (ii) State the principle illustrated by this experiment.

In Fig. A, B, C and D are four pendulums suspended from the same elastic string XY. The lengths of pendulum A and D are equal, while the length of pendulum B is shorter and of the pendulum C is longer. Pendulum A is set into vibrations.
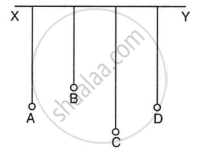
- What is your observation about the vibrations of pendulum D?
- Give reason for your observation in part (a).
- What type of vibrations take place in pendulums Band C?
- Give reason for the answer in part (c).
Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 3 Sound Exercise 1 [Page 148]
Differentiate between the following:
Light and sound waves.
Differentiate between the following:
Free and forced vibrations.
Differentiate between the following:
Radio waves and light waves.
Explain how is the principle of echo used by
(a) The bat during its flight at night,
(b) The dolphin to locate small fish as its prey.
Explain the following and illustrate your answer by drawing appropriate diagram:
Frequency
Explain the following and illustrate your answer by drawing appropriate diagram:
Loudness
Explain the following and illustrate your answer by drawing appropriate diagram:
Pitch
Explain the following and illustrate your answer by drawing appropriate diagram:
Quality of a musical note.
In fig. shows a snap shot of a wave from of frequency 50 Hz in a string. The numbers in the diagram represents distance in centimeters. Fpr the wave motion, find
(a) Wavelength,
(b) Amplitude,
(c) Velocity.
Name musical instrument, one in each case, which produces its notes by using the following. In each case state the method used to produce notes of different pitches and loudness.
(a) A vibrating string.
(b) A vibrating column air.
(c) Vibration of any other body.
Give scientific reason for the following:
Windows sometimes rattle when the low notes of a pipe organ are sounded.
Give scientific reason for the following:
When a nail is hammering appears to get higher and higher in pitch.
Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 3 Sound Exercise 2 [Page 149]
What determines the pitch of a sound?
How is it possible to recognize a person by his voice without seeing him?
How does the wave pattern of a loud note differ from a soft note? Draw a diagram.
Why is the loudness of the sound heard by a plucked wire increased when it is mounted on a sound board?
What change do you expect in the characteristics of a musical sound if
(i) Its frequency is increased,
(ii) Its amplitude is increased?
Comment on the statement 'loudness of sound is a subjective quantity, while intensity is an objective quantity.
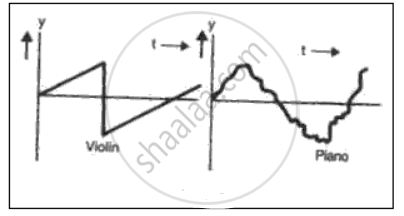
In fig. 2 two musical notes of the same pitch and same loudness are played on a violin and on a piano. Their wave forms are as shown in the diagram below. Explain why the wave patterns are different.
Solutions for 3: Sound
![Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 3 - Sound Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 3 - Sound - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-part-2-english-class-10-icse_6:39af211da77c495e91d1cf4305988990.PNG)
Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 3 - Sound
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Frank solutions for Mathematics Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE 3 (Sound) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Frank textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 3 Sound are Determination of Speed of Sound by the Method of Echo, Use of Echoes, Some Examples of Resonance, Sound, Difference Between the Sound and Light Waves, Reflection of Sound, Echoes, Natural Vibrations, Damped Vibrations, Forced Vibrations, Resonance, Demonstration of Resonance, Properties of Sounds, Loudness and Intensity, Pitch (or shrillness) and frequency, Audibility and Range, Quality (Or Timbre) and Wave Form, Noise Pollution, Noise and Music, Sound (Numerical).
Using Frank Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE solutions Sound exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Frank Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE students prefer Frank Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 3, Sound Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE additional questions for Mathematics Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
